-
-
Scientific LibraryAcute Coronary Syndrom ASCVD Prevention Bifurcation Stenting Cardio-Oncology Congestive Heart Failure DAPT Duration Drug Coated Balloon Fractional Flow ReserveNewsCases VideosE-LearningIndustry Insights
- LIVE
-
 Article Link
Article Link

ACC19 - Late Breaking Clinical Trails & Results Presentation
CBSMD
ASCVD Prevention
The Apple Heart Study- a new paradigm shift of future AFib monitoring?
The Apple Heart Study app uses data from Apple Watch to identify irregular heart rhythms, including those from potentially serious heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation. Apple is conducting this research study in collaboration with Stanford Medicine to improve the technology used to detect and analyze irregular heart rhythms, like atrial fibrillation - a leading cause of stroke.
Figure 1 illustratedby CBSMDafter the study design of Apple Heart Study.
Comments on the Apple Heart Study at ACC.19
1. The positive predictive value (PPV) for the tachogram was 71 percent and the PPV for notification was 84 percent. About half of participants receiving an irregular pulse notification contacted a study doctor.
2. Possible undetected AFib in subsequent ECG patch monitoring.
3. A high number of false positive heart rhythms that could then lead to further unnecessary tests and undue anxiety for patients.
4. The accuracy ofApple watchis still far short of more traditional and currently used monitoring techniques.
REDUCE-IT -Cardiovascular Risk Reduction with Icosapent Ethyl for Hypertriglyceridemia,a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving patients with established cardiovascular disease or with diabetes and other risk factors, who had been receiving statin therapy and who had a fasting triglyceride level of 135 to 499 mg per deciliter (1.52 to 5.63 mmol per liter) and a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level of 41 to 100 mg per deciliter (1.06 to 2.59 mmol per liter). The patients were randomly assigned to receive 2 g of icosapent ethyl twice daily (total daily dose, 4 g) or placebo. The primary end point was a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, coronary revascularization, or unstable angina. The key secondary end point was a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
Congestive Heart Failure
PIONEER-HF is a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double dummy, parallel group, active-controlled 8-week study to evaluate the effect of sacubitril and valsartan (LCZ696) versus enalapril on changes in NT-proBNP and safety and tolerability of in-hospital initiation of LCZ696 compared to enalapril in HFrEF patients who have been stabilized following hospitalization for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF).
MOMENTUM 3 -a multicenter study of MagLev technology in Patients undergoing mechanical circulatory support therapy with HeartMate 3.The goal of the trial was to evaluate treatment with a magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) compared with an axial-flow LVAD among heart failure patients requiring advanced mechanical support. The centrifugal-flow LVAD was designed to prevent disabling stroke or reoperation to replace or remove a malfunctioning device. Characteristics of the centrifugal-flow pump are wide blood passages to reduce shear stress, no mechanical bearings to reduce friction, and intrinsic pulse to prevent thrombosis.
Study Design-Randomized,Parallel.
Study Resultsof final report trial showed that a centrifugal-flow LVAD demonstrated superior performance to an axial-flow LVAD.
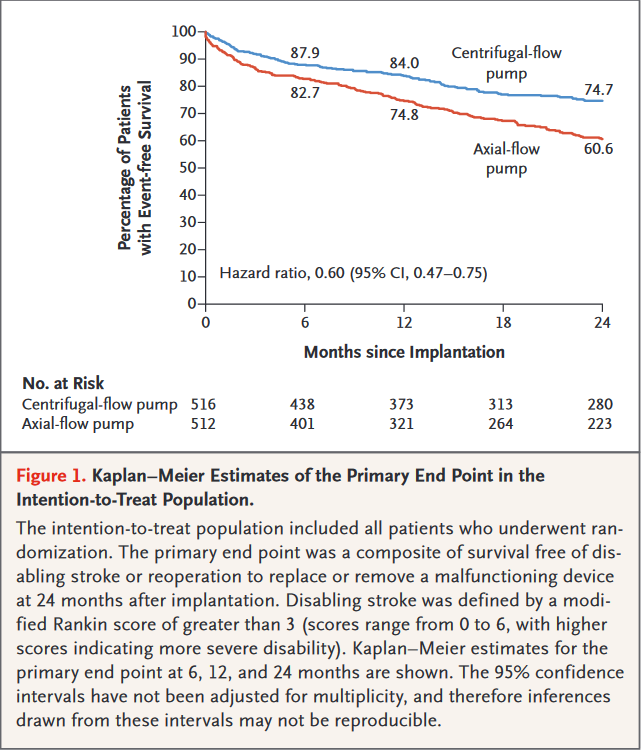

Principal Findings-The primary outcome, survival free from disabling stroke or reoperation to replace/remove a malfunctioning device at 24 months, occurred in 74.7% of the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 60.6% of the axial-flow pump group (p < 0.001 for superiority).
Secondary outcomes(actuarial)
- Overall survival at 24 months: 79.0% in the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 76.7% in the axial-flow pump group (p = 0.37)
- Any stroke at 24 months: 9.9% in the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 19.4% in the axial-flow pump group (p < 0.001)
- Disabling stroke at 24 months: 3.9% in the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 5.9% in the axial-flow pump group (p = not significant)
- Pump replacement at 24 months: 2.3% in the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 11.3% in the axial-flow pump group (p < 0.001)
- Any bleeding at 24 months: 43.7% in the centrifugal-flow pump group vs. 55.0% in the axial-flow pump group (p < 0.001)
Interpretation - Among patients with advanced heart failure, use of the HeartMate 3 centrifugal-flow pump was superior to the Heartmate II axial-flow pump at improving survival free from disabling stroke or reoperation. Overall survival was similar between the groups. The centrifugal-flow pump was also associated with a reduction in any stroke, any bleeding event, and reoperation for device malfunction.
Dual Anti-platelet Therapy
AUGUSTUS trial provides insight into the optimal oral antithrombotic therapy strategy for patients with AF and concomitant coronary artery disease. The unique2×2 factorial design will delineate the bleeding effects of various anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapies and generate evidence to guide the selection of the optimal antithrombotic regimen for this challenging group of patients. It is the largest and only prospective randomized trial to investigate in a blinded fashion the risk and benefits of aspirin on top of a non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant and P2Y12 receptor inhibition.
Study Results of "Antithrombotic Therapy after Acute Coronary Syndrome or PCI in Atrial Fibrillation" - Patients with both atrial fibrillation (AFib) and acute coronary syndrome (ACS) had a significantly reduced risk of bleeding when treated with apixaban vs. a vitamin K antagonist (VKA) and when taking placebo vs. aspirin.

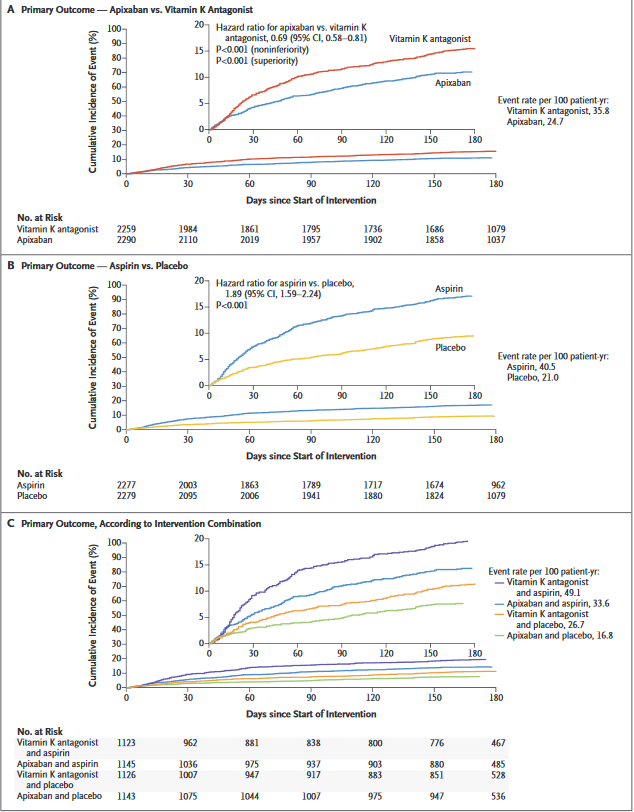
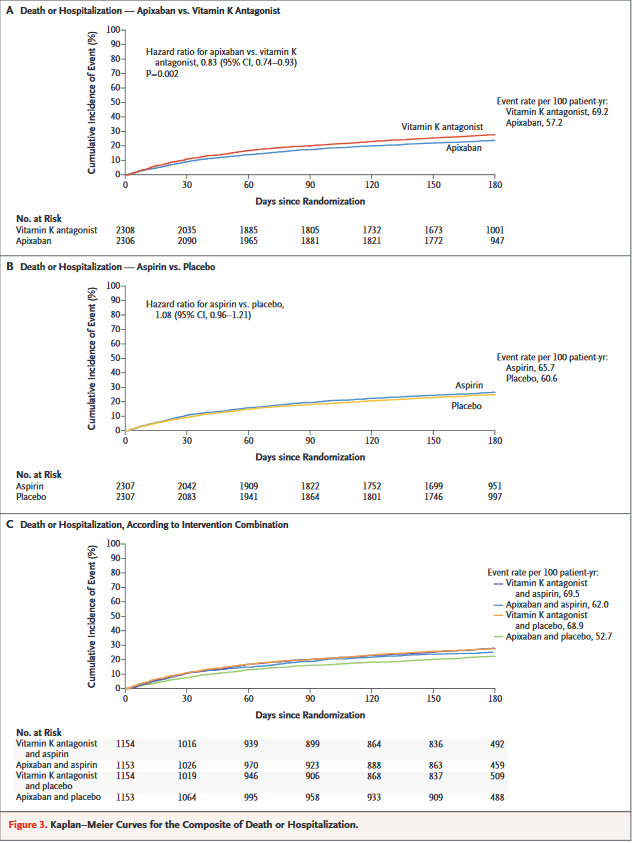
Comments on AUGUSTUS at ACC.19
Findings of AUGUSTUS show that the combination of apixaban and a drug such as clopidogrel – without aspirin – is the safest treatment regimen for this difficult-to-treat group of patients, without significantly increasing ischemic events such as heart attacks, strokes and blood clots.
GLOBAL LEADERS trial failed to show that 1 month of aspirin plus ticagrelor followed by 23 months of ticagrelor monotherapy (n =
7,980) was superior to 1 year of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) (aspirin plus either clopidogrel or ticagrelor) followed by 1 year of aspirin monotherapy (n = 7,988) among patients with stable or unstable coronary disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with a biolimus-eluting stent at preventing
adverse events.
Study Design
- Randomized
- Parallel
- Stratified
- Concealed

Secondary outcomes
- - All-cause mortality: 2.8% of the experimental group vs. 3.2% of the control group (p = 0.18)
- - Myocardial infarction: 1.0% of the experimental group vs. 1.3% of the control group (p = 0.14)
- - Grade 3 or 5 bleeding: 2.0% of the experimental group vs. 2.1% of the control group (p = 0.77)
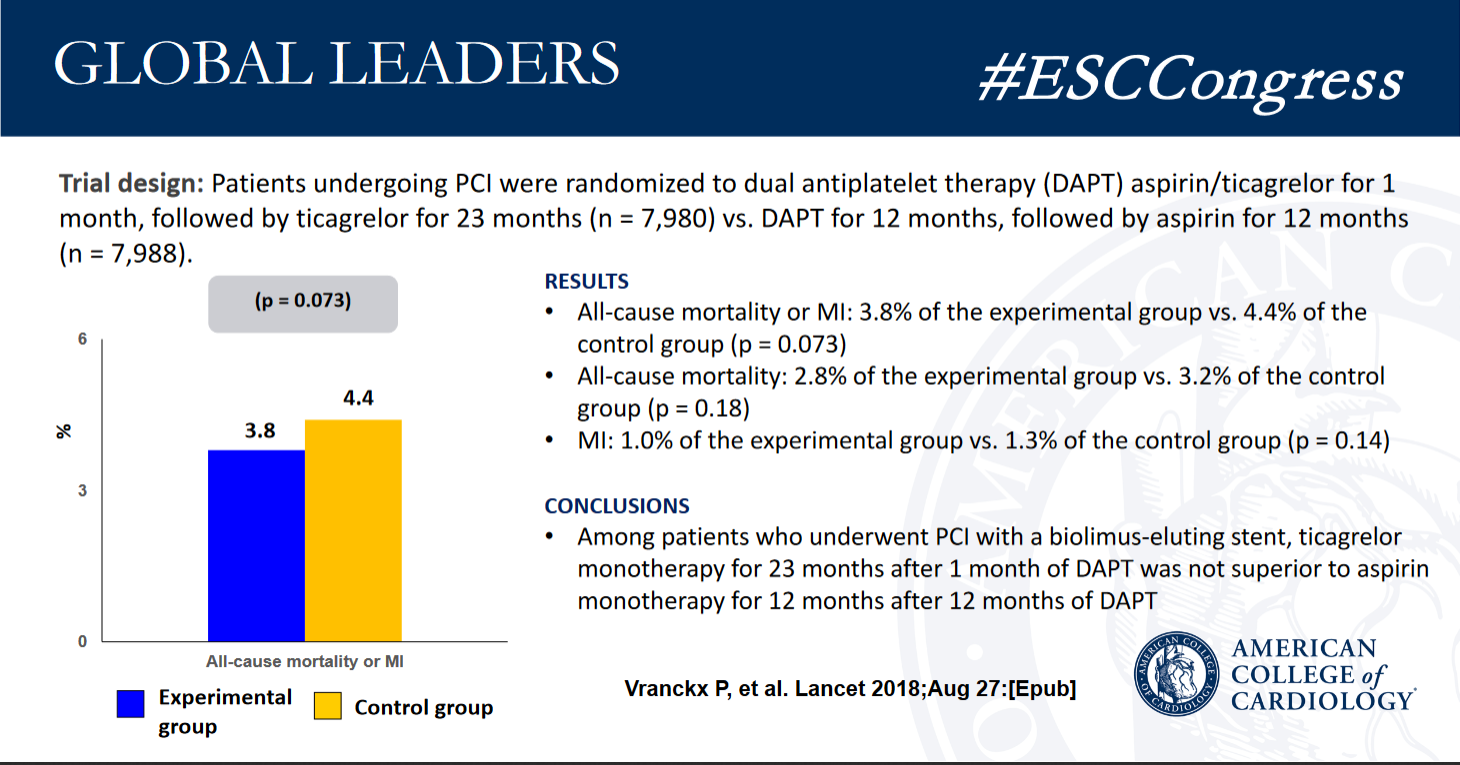
Among patients who underwent PCI with a biolimus-eluting stent, 1 month of DAPT followed by ticagrelor monotherapy for 23 months after 1 month of DAPT was not superior to 12 months of DAPT followed by aspirin monotherapy for 12 months after 12 months of DAPT. The composite outcome, components of the primary outcome, and major bleeding were similar between treatment groups.
The GLOBAL LEADERS Adjudication Sub-StudY (GLASSY), a prospective substudy of clinical endpoint adjudication processes within an investigator-reported randomised controlled trial in patients with coronary artery disease of GLOBAL LEADERS trial was also presented at ACC.19.
The GLASSY sub-study examined centrally adjudicated outcomes rather than investigator reported events:
- - All-cause death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or urgent target vessel revascularization (primary efficacy endpoint for GLASSY): 7.1% of the experimental group vs. 8.4% of the control group (p for noninferiority < 0.001)
- - Landmark analysis at 1 year revealed enhanced benefit favoring the experimental group for the outcome of definite stent thrombosis
- - Grade 3 or 5 bleeding: 2.5% of the experimental group vs. 2.5% of the control group (p = 0.99)
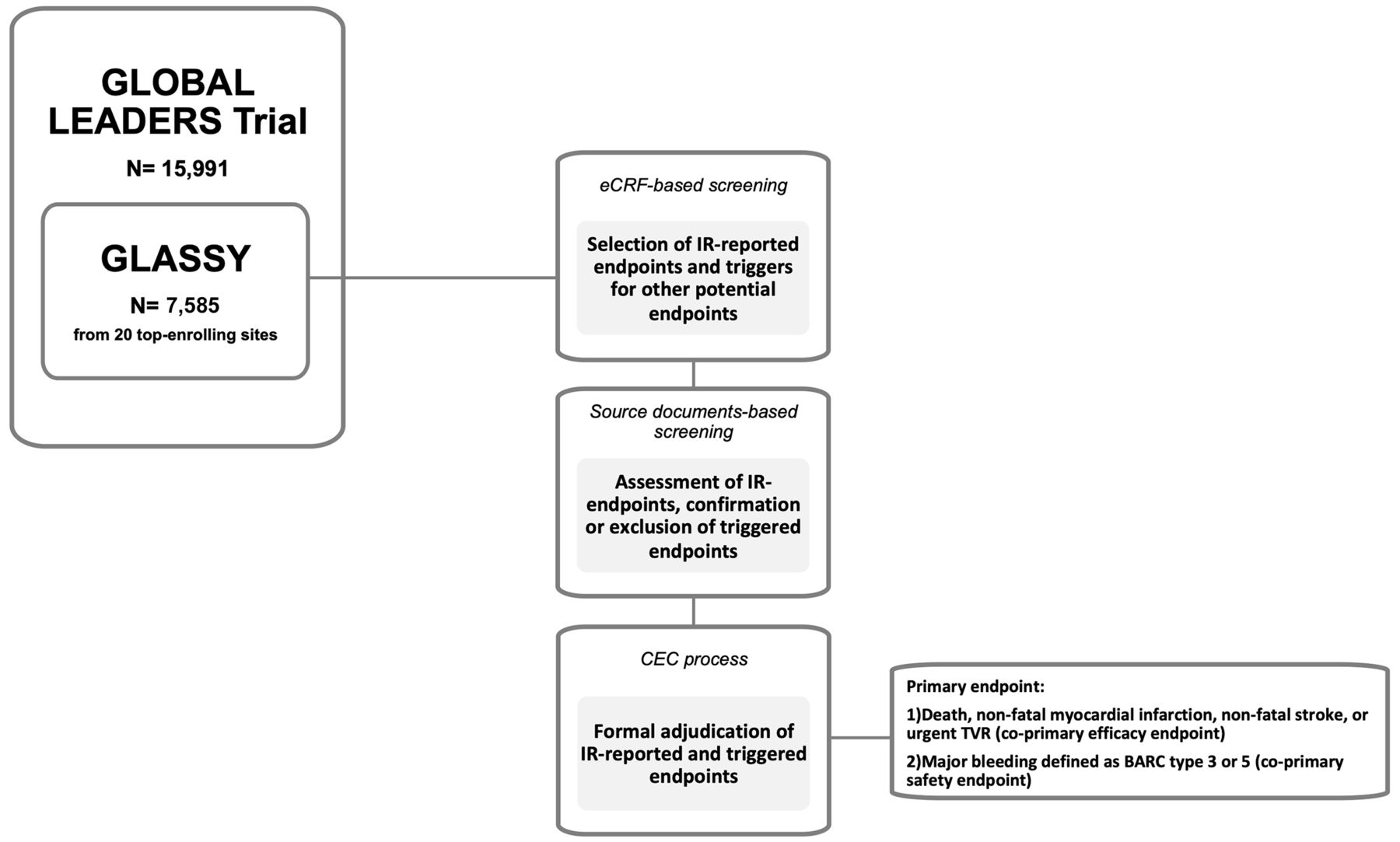
The GLASSY sub-study revealed that 1 month of DAPT was noninferior to 12 months of DAPT at preventing death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or urgent target vessel revascularization. The experimental strategy of a shorter duration of DAPT did not increase ischemic events and may have even reduced the incidence of stent thrombosis without increasing bleeding events.
The SMART-CHOICE trial is a prospective, open-label, multi-center, and randomized study designed to test the non-inferiority of P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy compared with aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor after mandatory 3-month DAPT in patients undergoing PCI with current-generation DES.
STOPDAPT-2 trial , a randomized parallel trail showed that 1-month DAPT was superior to 12-month DAPT at preventing net adverse ischemic events among patients undergoing DES-PCI.
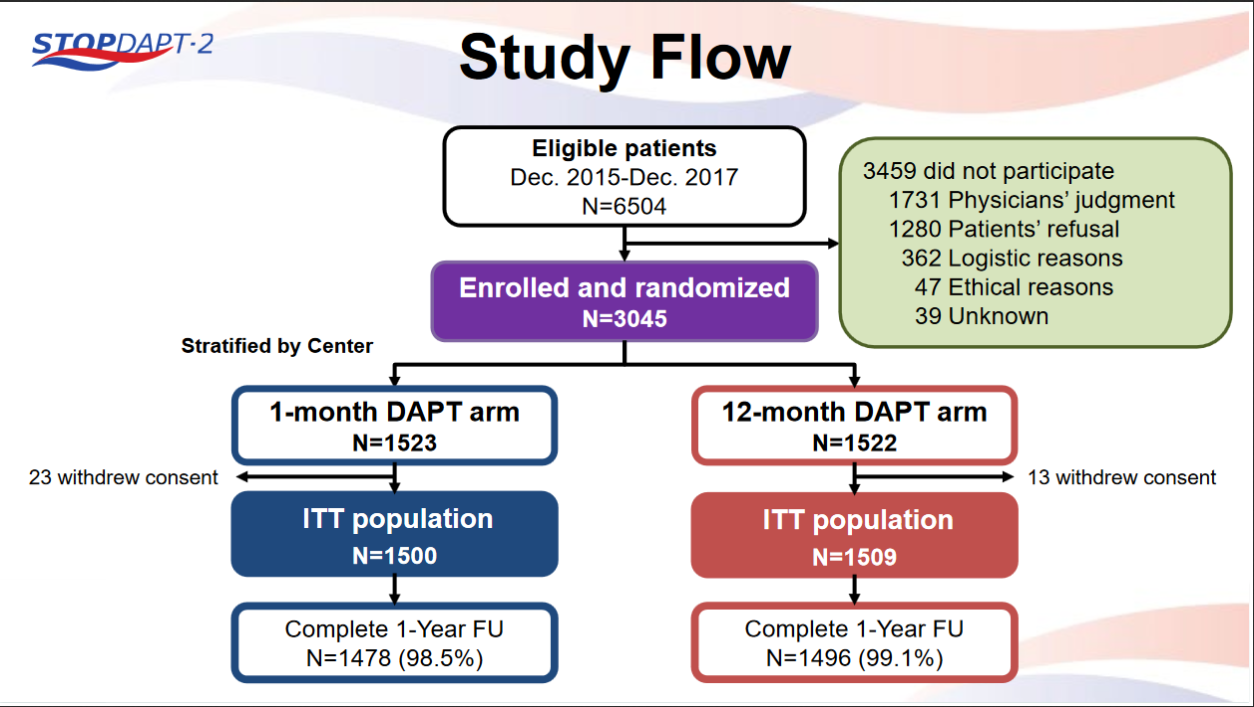
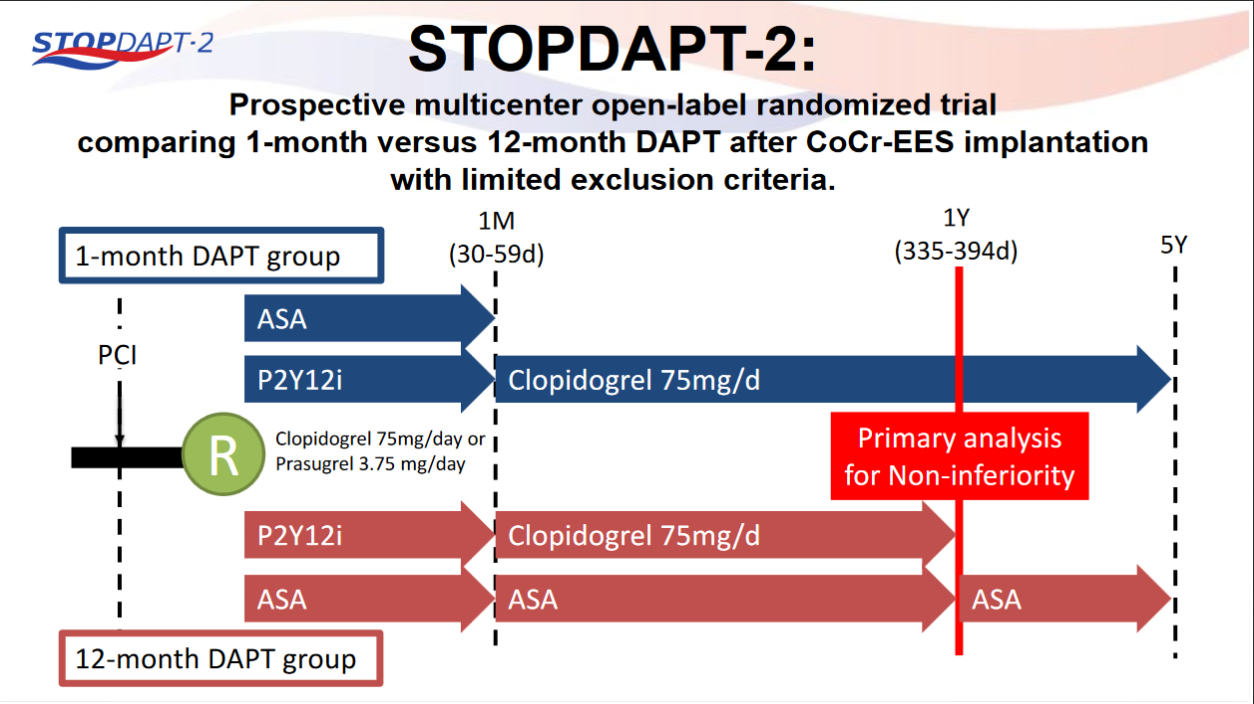
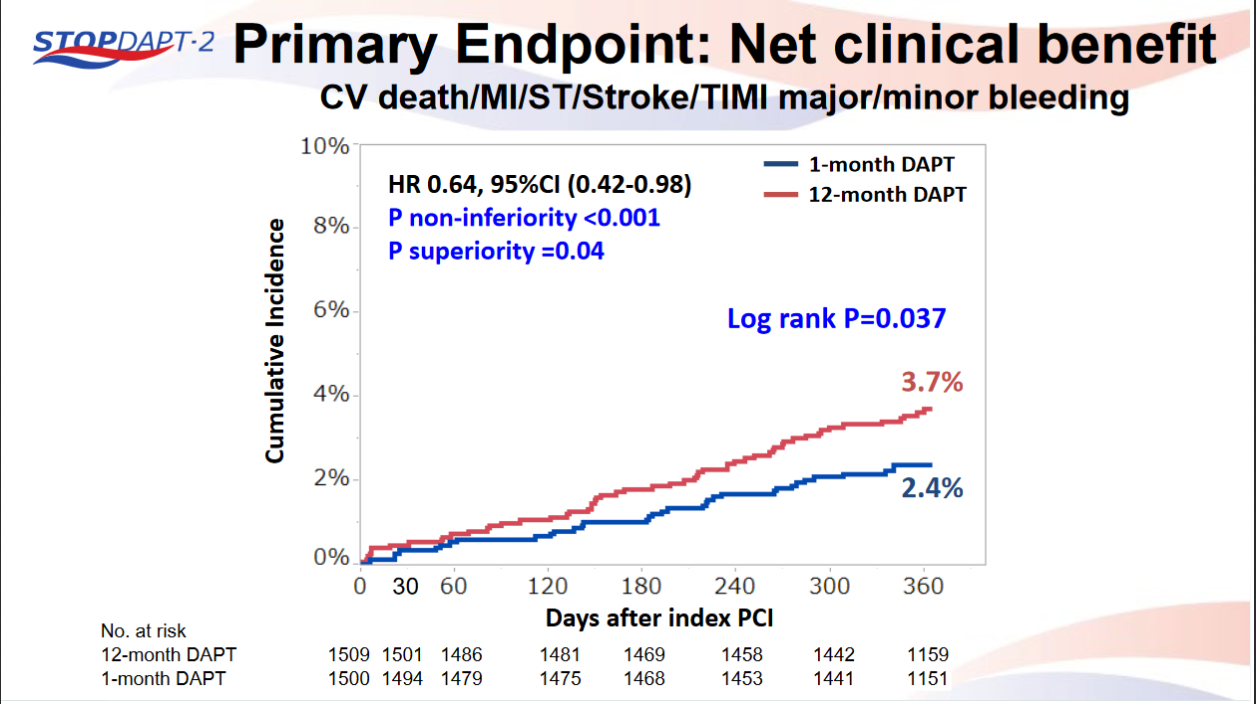

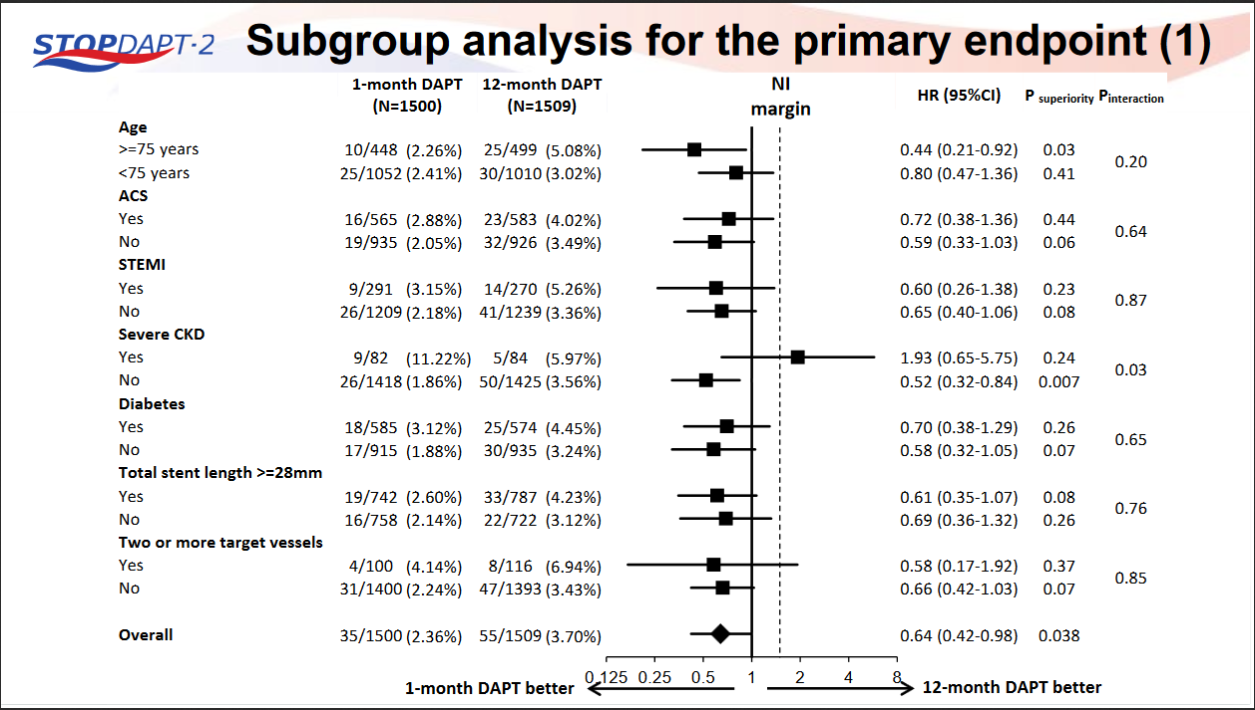
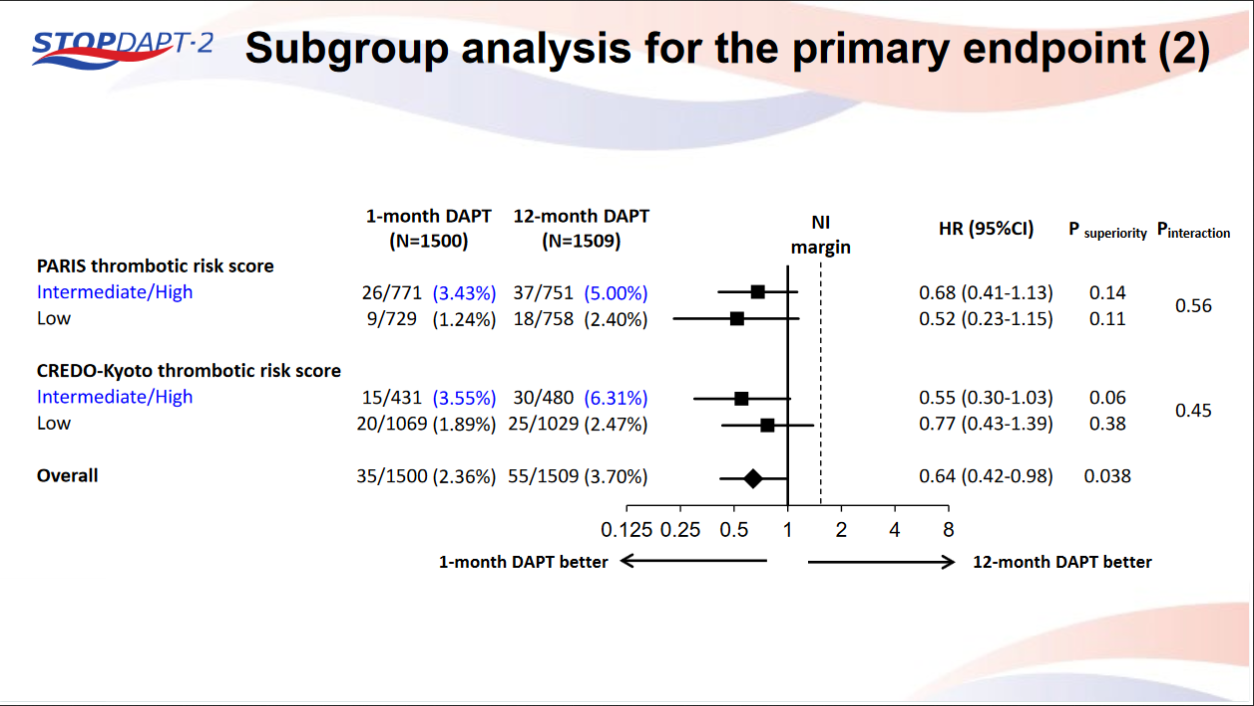
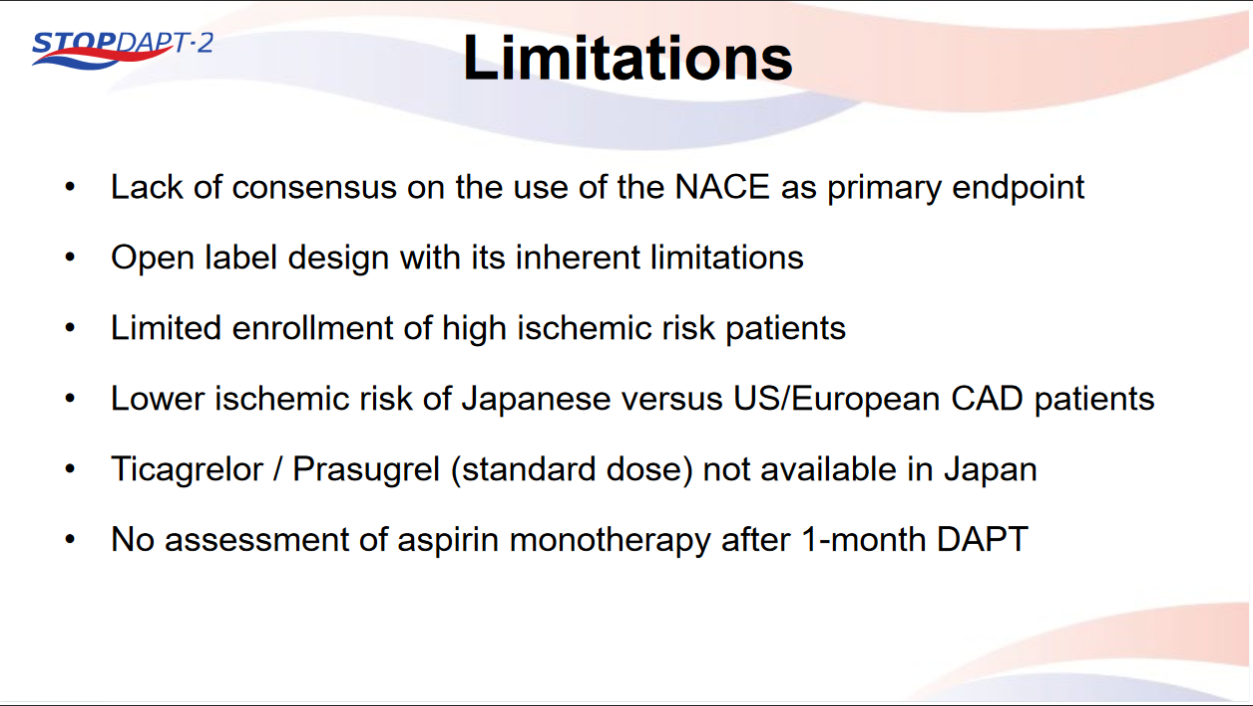
Please click on STOPDAPT Study to view the study results of 3 months DAPT vs. 12 month DAPT results published in year 2016.
Percutanous Coronary Intervention
COACT : Coronary Angiography After Cardiac Arrest Without ST-Segment Elevation - first published randomized clinical trial evaluating the strategy of immediate coronary angiography versus delayed coronary angiography in patients successfully resuscitated after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with an initial shockable rhythm and no ST-segment elevation on their electrocardiogram. A total of 552 patients was randomized. The primary endpoint was survival at 90 days, at which time 64.5% (176/273) of patients receiving immediate angiography and 67.2% (178/265) of patients in the delayed angiography group were alive (odds ratio 0.89; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.62-1.27; p = 0.51).
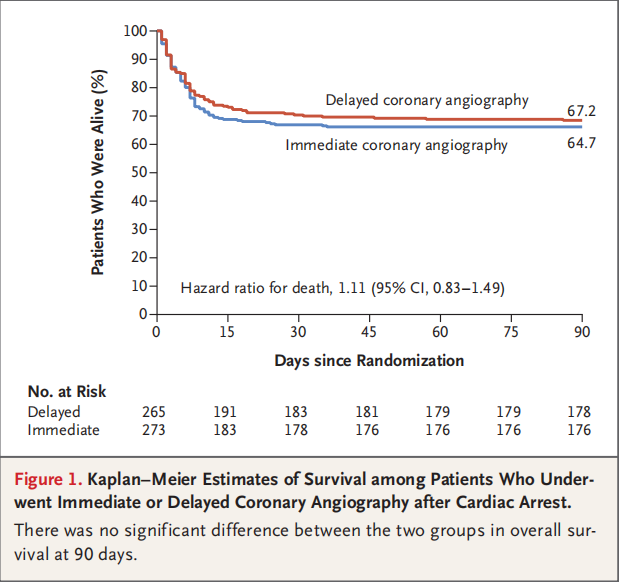
1. Both arms of COACT trail had excellent 90-day survival rates;
2. only 5% of acute coronary thrombotic occlusion found among these resuscitated cardiac arrest patients;
3.
The DEFINE PCI Trial- blinded physiologic assessment of residual ischemia after successful angiographic percutaneous coronary intervention. Abstract embargoed at this time.
Vascular Complication During Percutanous Coronary Intervention
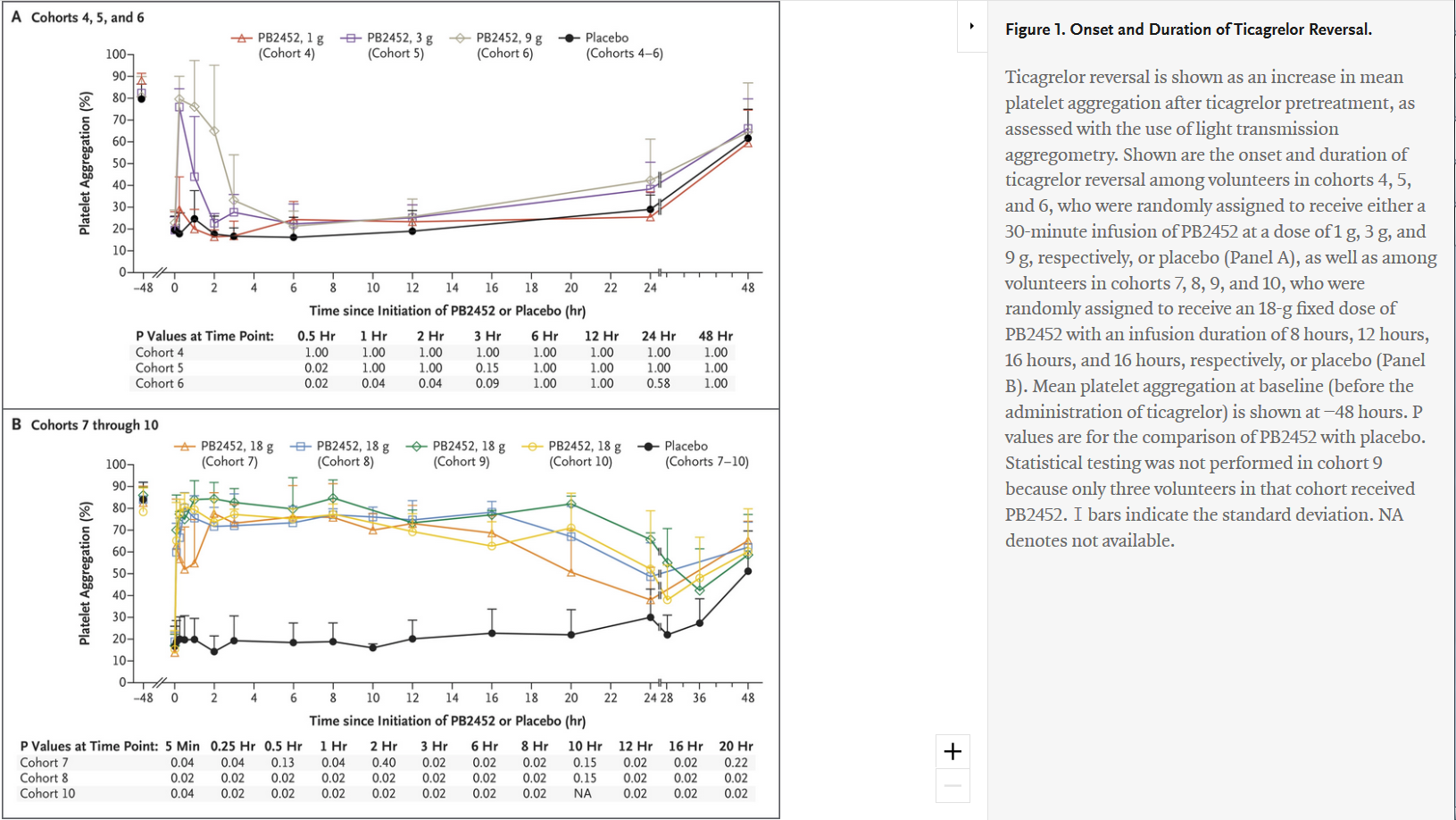
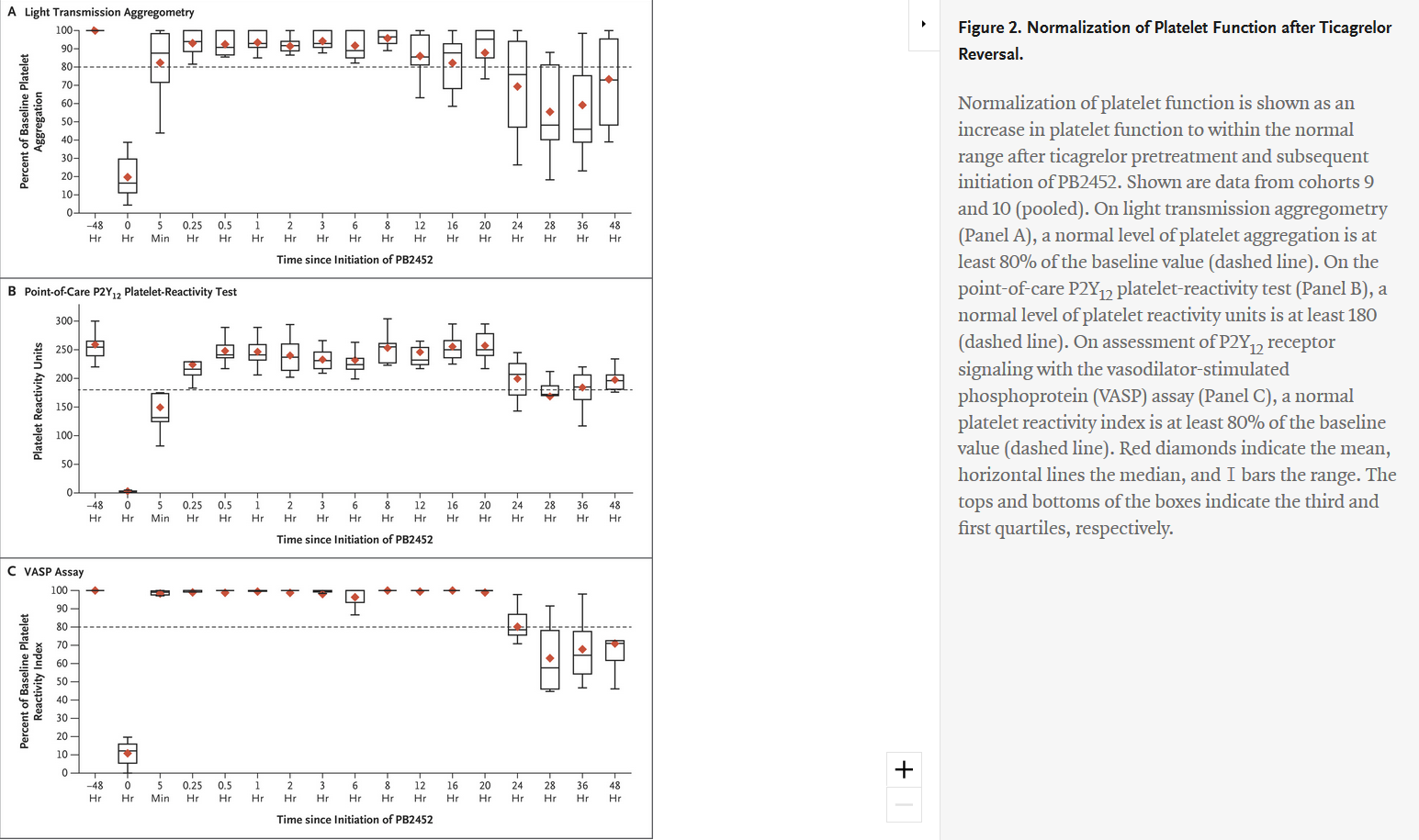
"Antibody-Based Ticagrelor Reversal Agent in Healthy Volunteers" - evaluated intravenous PB2452 as a ticagrelor reversal agent and assessed platelet function in 64 healthy volunteers before and after 48 hours of ticagrelor pretreatment, and again after the administration of PB2452 or placebo. Of the 64 volunteers who underwent randomization, 48 were assigned to receive PB2452 and 16 were assigned to receive placebo. Results showed that after 48 hours of ticagrelor pretreatment, platelet aggregation was suppressed by approximately 80 percent. As measured by multiple assays, PB2452 administered as an initial intravenous bolus followed by a prolonged infusion (8, 12 or 16 hours) was found to be associated with a significantly greater increase in platelet function than placebo. Furthermore, ticagrelor reversal occurred within five minutes after the initiation of PB2452 and was sustained for more than 20 hours.
Comments at on PB2452 May Reverse Antiplatelet Effects of Ticagrelor at ACC.19 - "The ability to reverse the action of novel oral anticoagulants has been a major advance in antithrombotic therapy."
Transradial Access Strategy Provides Most Benefit for PCI-Related Bleeding
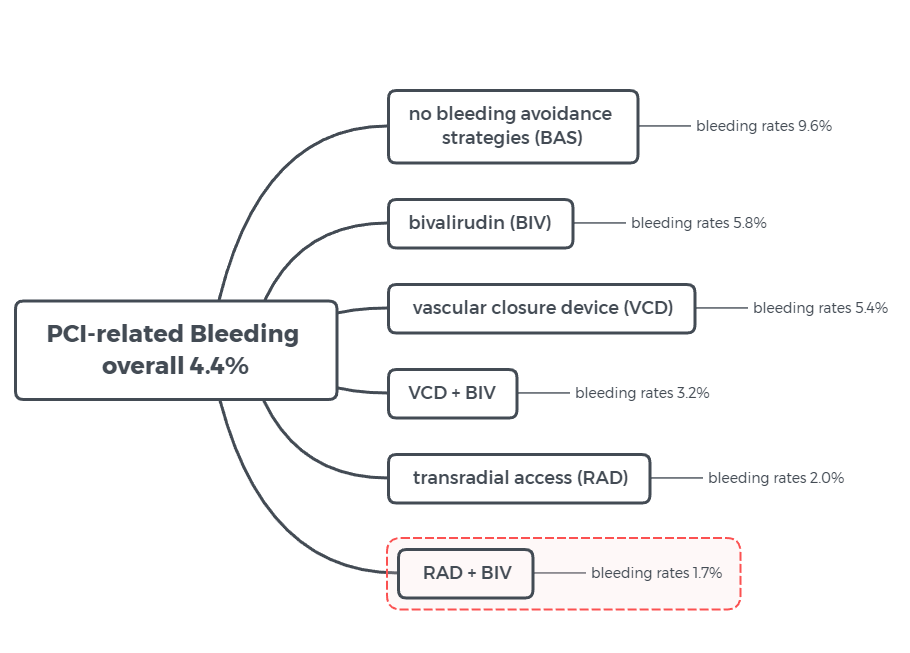
Figure 2 illustratedby CBSMD after study results of according to a poster research presented March 16 at ACC.19 in New Orleans, LA.

http://www.cbsmd.cn Contact us by cbs@cbsmd.cn
Copyright ⓒ CBSMD Nanjing China. All rights reserved.