- NEWS
-
-
Scientific LibraryAcute Coronary Syndrom ASCVD Prevention Bifurcation Stenting Cardio-Oncology Congestive Heart Failure DAPT Duration Drug Coated Balloon Fractional Flow ReserveCases VideosE-LearningIndustry Insights
- LIVE REVIEW
-
 Article Link
Article Link

EUROPCR 2019 - Stenting for Bifurcation Leisons
CBSMD
Treatment of Coronary bifurcation DKCRUSH-II 5 years
OBJECTIVE - to report the clinical outcomes of double kissing crush (DK crush) vs provisional stenting (PS) of coronary bifurcation lesions
STUDY DESIGN - multicenter randomized trail
POPULATION - symptomatic patients with Medina 1,1,1 or 0,1,1 bifurcation lesions
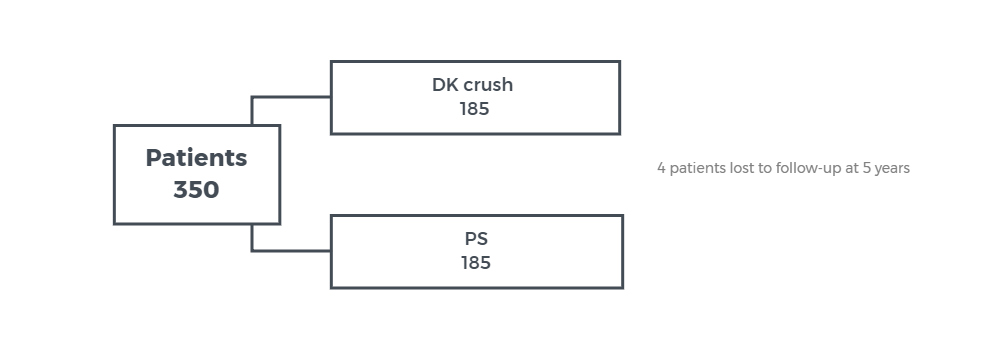 RESULTS - MACE at 5 years 15.7% for DK crush group and 23.8% for PS group, HR =1.67 (95% CI ; 0.99 -2.83), p= 0.051
RESULTS - MACE at 5 years 15.7% for DK crush group and 23.8% for PS group, HR =1.67 (95% CI ; 0.99 -2.83), p= 0.051
CONCLUSION - the DK crush technique is associated with a lower 5-year MACE rate as compared to provisional stenting for treatment of bifurcation lesions.
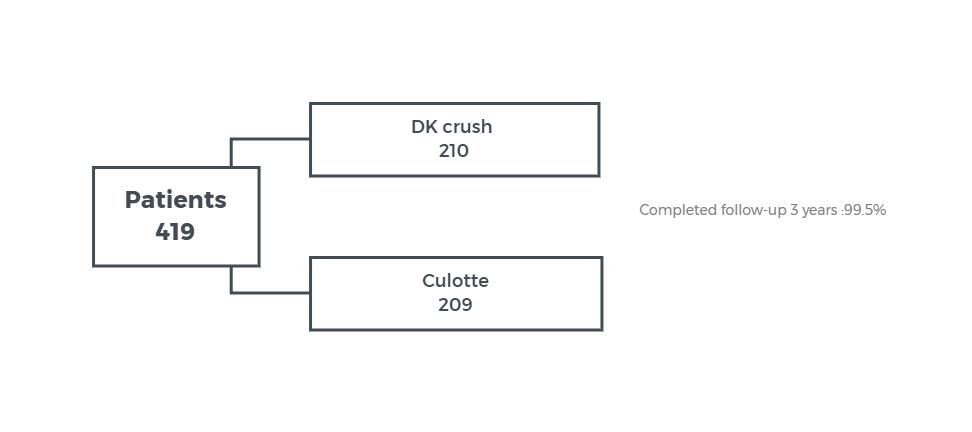
OBJECTIVE - to report the differences in clinical outcomes of treatment of distal left main bifurcation lesions with double kissing crush vs culotte stenting technique
STUDY DESIGN - prospective multicenter randomized study
POPULATION - patients with distal left main bifurcation Medina 1,1,1 or 0,1,1
ENDPOINTS - MACE as composite of cardiac death, MI or TVR at 3 years.
 |
|
|
RESULTS - MACE rate at 3 year: 8.2% for DK crush stenting vs. 23.7% for culotte stenting |
|
|
3-year outcome |
DK Crush |
Culotte |
p-value |
|
Death % |
1.4 |
2.9 |
0.34 |
|
MI % |
3.4 |
8.2 |
0.037 |
|
TVR % |
5.8 |
18.8 |
<0.001 |
|
Definite ST % |
0 |
3.4 |
0.007 |
CONCLUSION - DK crush stenting for distal left main bifurcation lesions is associated with better 3-year clinical outcome than culotte stenting.
Double Kssing Crush vs. provisional stenting for left main bifurcations : DKCRUSH-V
OBJECTIVE - to determine whether DK crush - 2 stent technique is superior to PS for treatment of bifurcation lesions
STUDY DESIGN - prospective, randomized international multicenter trail
POPULATION - symptomatic patients (stable, unstable AMI > 24h) with left main bifurcation lesions (Medina 1,1,1 or 0,1,1)
ENDPOINTS - target lesion failure: cardiac death, TV-MI or clinical TLR at 12 months
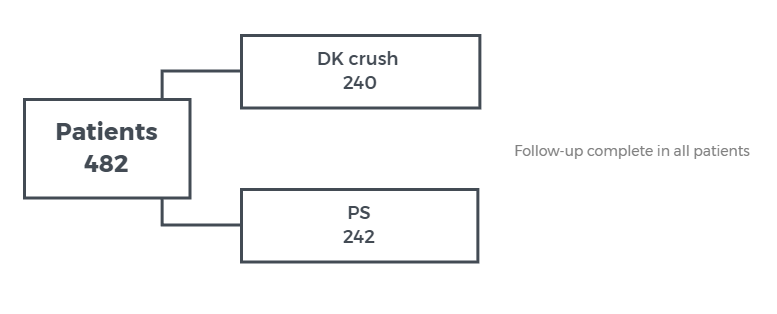
RESULTS - TLR at 1-year: 5.0% for DK crush group vs. 10.7% for PS group, HR = 0.42, 95% CI 0.21 - 0.85, p=0.02
CONCLUSION - a planned DK crush - 2 stent technique was superior to provisional stenting for the treatment of left main bifurcation lesions.
Bifurcation stent vs provisional stenting for bifurcation lesions: TRYTON
OBJECTIVE - to compare the outcome of a dedicated bifurcation stent ( TRYTON Medical) with side-branch balloon angioplasty with DES for treatment of left main bifurcation lesions
STUDY DESIGN - single blind, multicenter, randomized trial - non-inferiority with margin 5.5%
POPULATION - patients with de novo true left main bifurcation lesion
ENDPOINTS - TVF: cardiac death, MI, clinical driven TVR (MB or SB) at 9 months
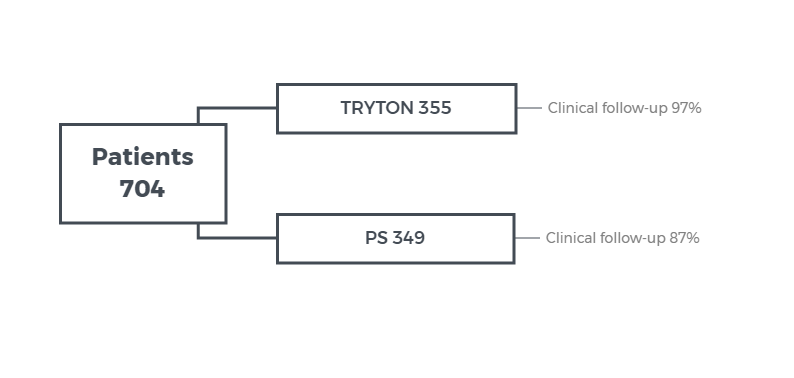
RESULTS - TVF at 9-months 17.4% for TRYTON group vs. 12.8% for provisional group, pnon-inferiority= 0.42 (not within 5.5% margin), p=0.11; SB in-segment diameter restenosis at 9 months, 31.6% for TRYTON vs. 38.6% for provisional group, p=0.002
CONCLUSION - provisional stenting is preferred strategy over TRYTON for treatment of left main bifurcation lesions.
Provisional T- stenting vs routine T-stenting: BBK-1 5 years
OBJECTIVE - to compare the 5-year clincial outcome of treatment of de novo bifurcation lesions with provisional T-stenting as compared with routine T-stenting
STUDY DESIGN - multicenter randomized trial
POPULATION - patients with de novo bifurcation lesions
ENDPOINTS - incidence of target lesion revascularization at 5 years
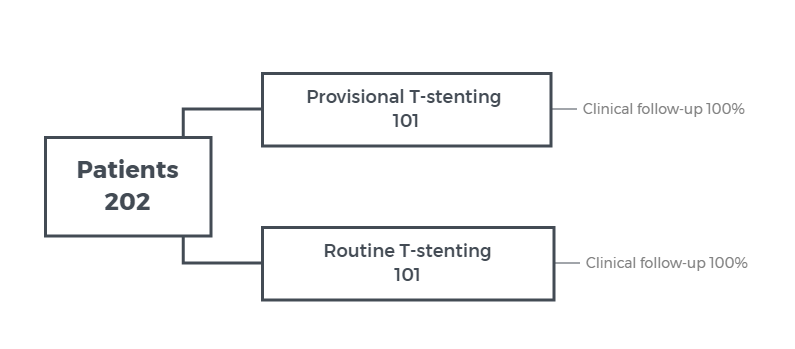
RESULTS - TLR at 5-year 16.2% for provisional T- stenting vs 16.3% for routine T-stenting, p=0.97
CONCLUSION - the 5-year TLR rate was similar using provisional T- stenting compared to routine T-stenting for de novo left main bifurcation lesions.
Bifurcation lesions: SMART-STRATEGY 3 years
OBJECTIVE - to report the 3-year clinical outcome of a conservative strategy compared to aggressive strategies for provisional side branch intervention
STUDY DESIGN - non-blinded, single center, randomized trial
POPULATION -patients with stable angina or NSTEMI and large de novo bifurcation lesion
ENDPOINTS - TVF as composite cardiac death, MI or TVR at 3-years
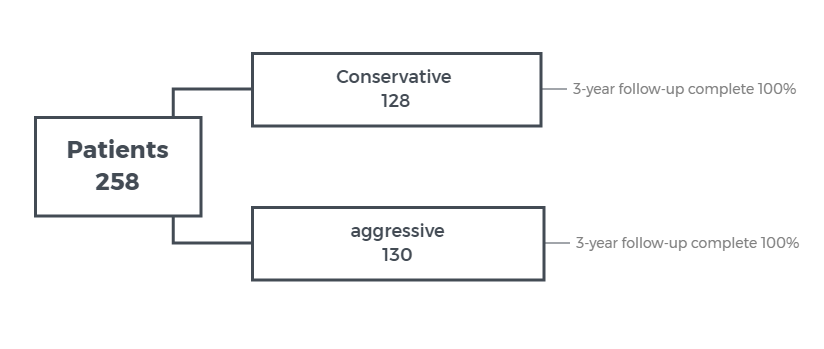
RESULTS - TVF at 3-year 11.7% for conservative strategy vs 20.8% for aggressive strategy, p=0.049
CONCLUSION - a conservative strategy for provisional SB intervention is associated with better 3-year outcome compared to an aggressive strategy.
Bifurcation lesion treatment : EBC Two Study
OBJECTIVE - to compare a provisional strategy with a systematic 2-stent technique for percutanous treatment of true bifurcation lesions with significant large sized ostial disease length side branches
STUDY DESIGN - multicenter randomized control study
POPULATION - symptomatic patients with true bifurcation lesions: SB diameter
≥ 2.5mm, ostial disase length ≥ 5mm
ENDPOINTS - composite of death, MI and TVR at 12 months
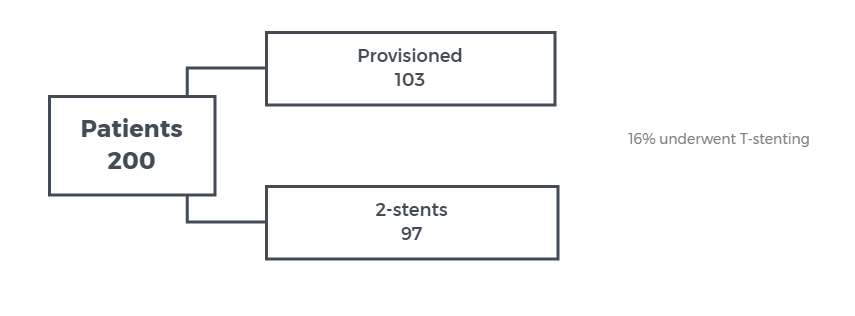
RESULTS - Primary endpoint at 12 months 7.7% for provisional group vs 10.3% for 2-stent technique, HR=1.02, 95% CI 0.78-1.34, p=0.53
CONCLUSION - the composite death, MI and TVR at 12 months is not different between provisional stenting and 2-stent technique for treatment of true bifurcation leisons.