Other Relevant Articles
Review Article2017 Jul 11;70(2):196-211.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Sack MN, Fyhrquist FY, Kovacic JC et al. Keywords: apoptosis; mitochondria; necrosis; reactive oxygen species; senescence; sirtuin; telomere
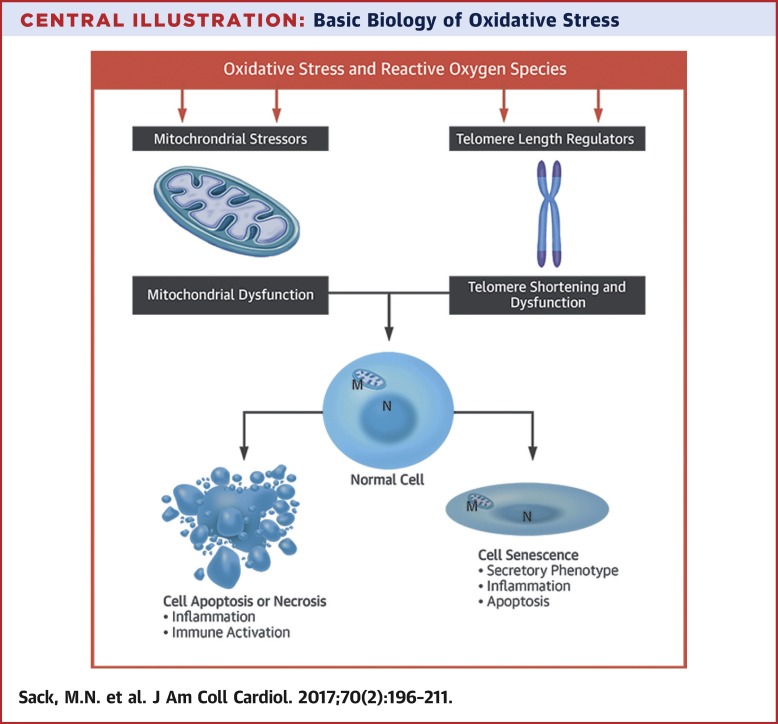
The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a fundamental aspect of normal human biology. However, when ROS generation exceeds endogenous antioxidant capacity, oxidative stress arises. If unchecked, ROS production and oxidative stress mediate tissue and cell damage that can spiral in a cycle of inflammation and more oxidative stress. This article is part 1 of a 3-part series covering the role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease. The broad theme of this first paper is the mechanisms and biology of oxidative stress. Specifically, the authors review the basic biology of oxidative stress, relevant aspects of mitochondrial function, and stress-related cell death pathways (apoptosis and necrosis) as they relate to the heart and cardiovascular system. They then explore telomere biology and cell senescence. As important regulators and sensors of oxidative stress, telomeres are segments of repetitive nucleotide sequence at each end of a chromosome that protect the chromosome ends from deterioration.