DAPT Duration
Clinical TrialVolume 70, Issue 15, October 2017
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Giustino G, Mehran R, Stone GW et al. Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; average daily rate; bleeding events; ischemic events; percutaneous coronary intervention
BACKGROUND - The risk of recurrent ischemic and bleeding events after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) may not be uniform over time, which may affect the benefit-to-risk ratio of guideline-recommended antithrombotic therapies in different intervals.
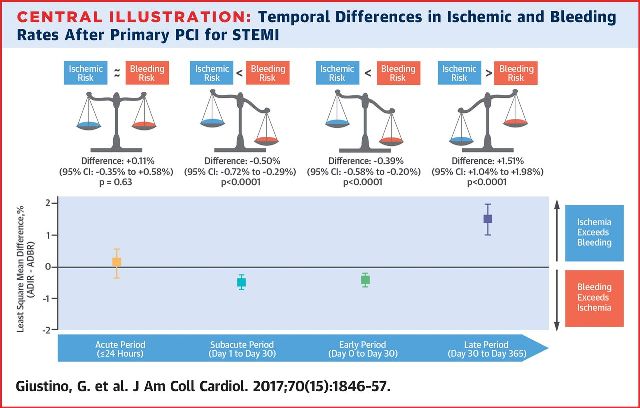
OBJECTIVES - This study sought to characterize the average daily ischemic rates (ADIRs) and average daily bleeding rates (ADBRs) within the first year after primary PCI for STEMI.
METHODS - Among 3,602 patients with STEMI who were enrolled in the HORIZONS-AMI (Harmonizing Outcomes with Revascularization and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction) trial, all ischemic and bleeding events, including recurrent events, were classified according to the timing of their occurrence as acute (≤24 h after PCI), subacute (1 day to 30 days), and late (30 days to 1 year). Patients were treated with aspirin and clopidogrel for the entire year. ADIRs included cardiac death, reinfarction, and definite stent thrombosis. ADBRs included non–coronary artery bypass graft–related Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction major and minor bleeding. ADIRs and ADBRs were calculated as the total number of events divided by the number of patient-days of follow-up in each interval assuming a Poisson distribution. Generalized estimating equations were used to test the absolute least square mean differences (LSMD) between ADIRs and ADBRs.
RESULTS- The ADIR and ADBR both exponentially decreased from the acute to the late periods (p < 0.0001). Although there were no significant differences in ADIR and ADBR in the acute phase (LSMD: +0.11%; 95% confidence interval [CI]: −0.35% to 0.58%; p = 0.63), the ADBR was greater than the ADIR in the subacute phase (LSMD: −0.39%; 95% CI: −0.58% to −0.20%; p < 0.0001). In the late phase, the ADIR exceeded the ADBR (LSMD: +1.51%; 95% CI: 1.04% to 1.98%; p < 0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS - After primary PCI, the ADIR and ADBR both markedly decreased over time. Although the rates for bleeding exceeded those for ischemia within 30 days, the daily risk of ischemia significantly exceeded the daily risk of bleeding beyond 30 days, supporting the use of intensified platelet inhibition during the first year after STEMI.