
科学研究
Original Research
JOURNAL: Article Link
jiangxiao
HOT TOPIC 1 - Time of Revascularization in STEMI Patients
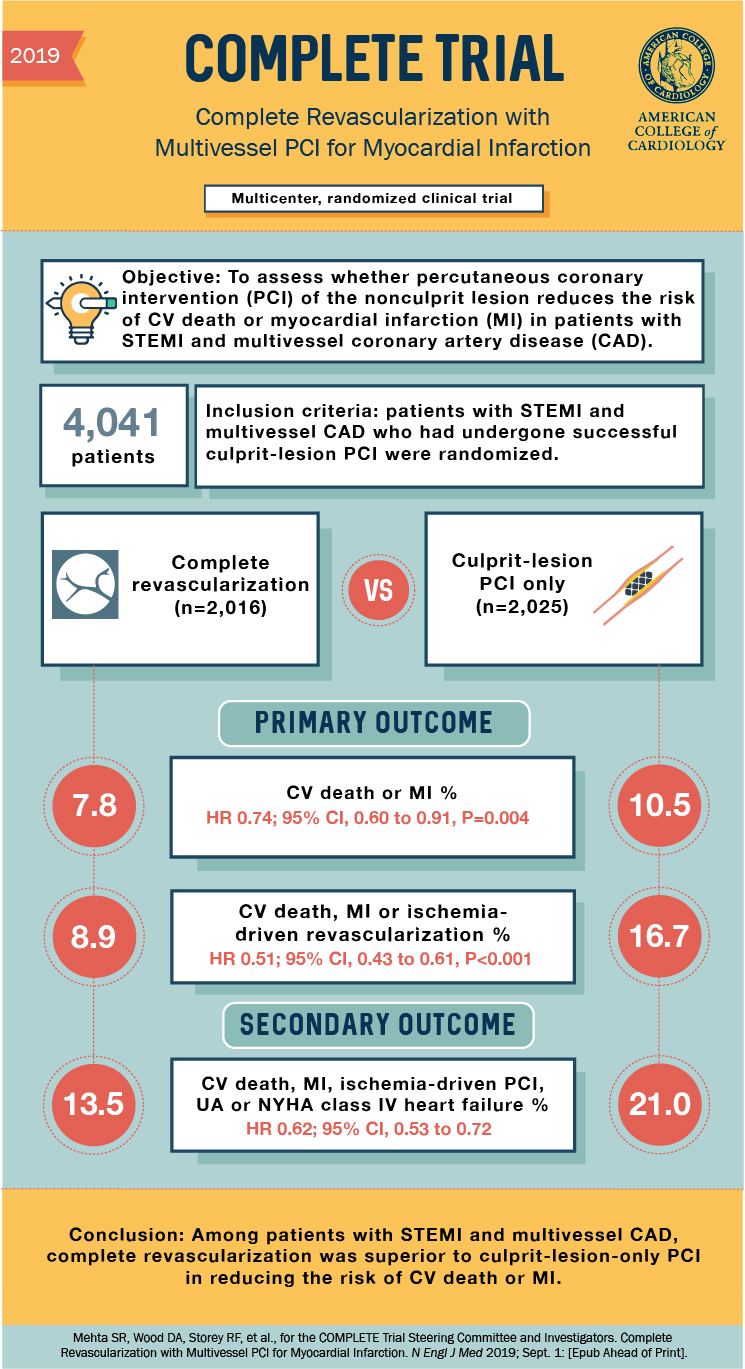
COMPLETE研究(Complete revascularization with Multivessel PCI for MI)对比了STEMI患者中仅对罪犯血管血运重建和分期完全血运重建的优劣。这项研究旨在通过在该领域最大样本量(N=4000)明确分期血运重建对非合并心源性休克的患者是否可行,具体研究结果详见图一。 现有欧洲的指南已经更新,认为完全血运重建优于仅对罪犯血管病变进行血运重建,但并未指出对非罪犯血管病变的合适的治疗时间。在接受一次PCI治疗的STEMI合并多支血管疾病患者中,完全血运重建优于单纯的罪犯血运重建。完全血运重建与心血管疾病死亡或心肌梗死的减少有关。前期试验已经证明了完全血运重建的获益,但其获益归根于血运重建次数的降低。COMPLETE研究则显示完全血管重建与主要研究终点心血管死亡或心肌梗死的等硬终点的减少相关。总之,完全血管重建于STEMI患者直接经皮冠状动脉介入术(PPCI) 是有益的。
图一
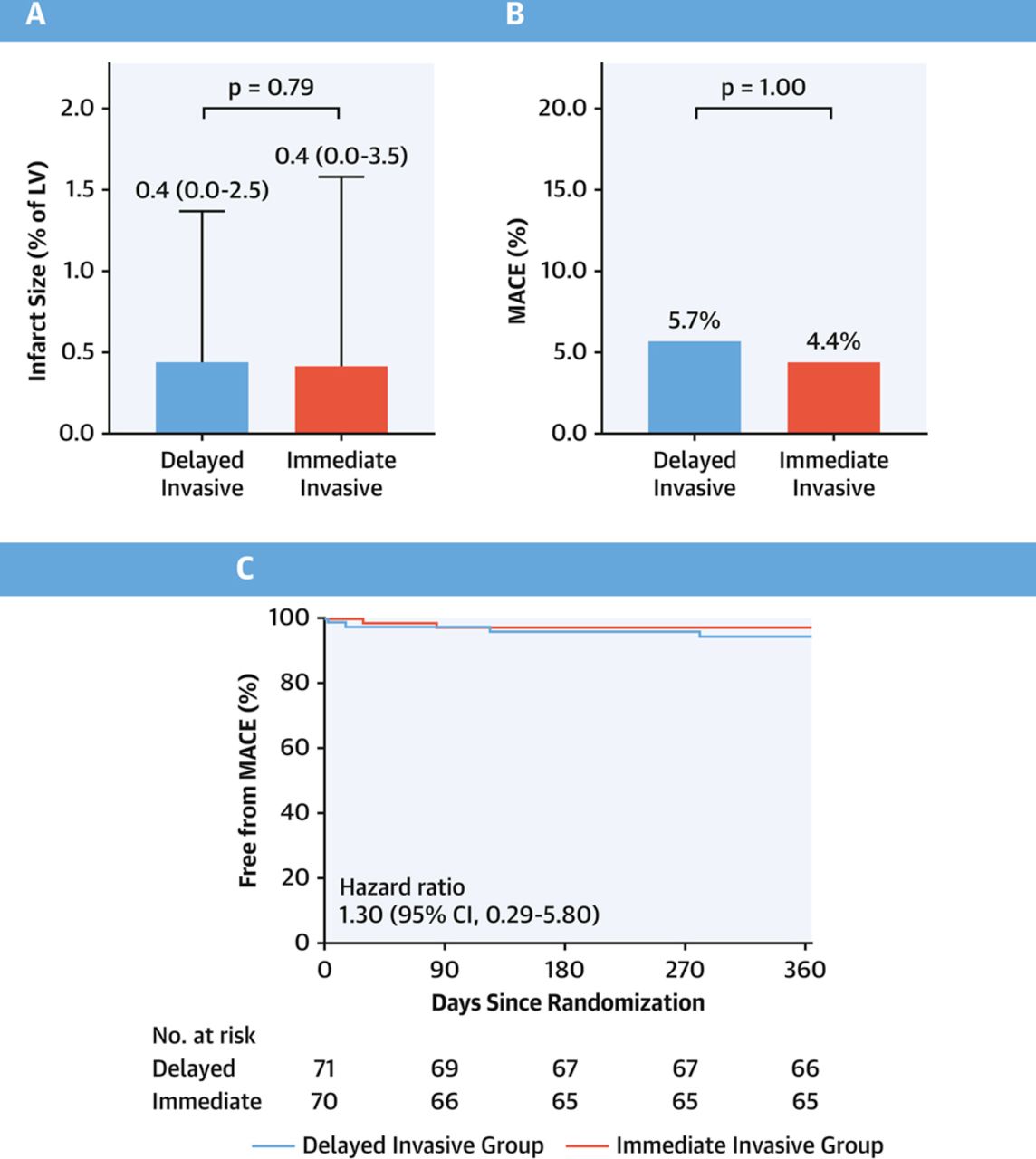
ESC 2019大会上荷兰阿姆斯特丹研究团队在多中心对ACS合并发生短暂性STEMI(transient STEMI)患者以1:1小样本随机设计检验了延迟冠脉介入(delayed coronary intervention)对比即刻干预(immediate coronary intervention)的1年预后,“1-Year Outcomes of Delayed Versus Immediate Intervention in Patients With Transient ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction”研究结果详见图二。
图二
ESC 2019上发布的最新STEMI血运重建策略/时机证据已同步到前期导读文章“Complete Revascularization Versus Culprit Lesion Only in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Multivessel Disease”。
HOT TOPIC 2 - Genotype Guided P2Y12 in ACS Patients
创新抗凝血疗法高选择性P2Y12受体拮抗剂Selatogrel的II期临床数据在ESC 2019期间发表, P2Y12受体是主要表达在血小板表面的G蛋白偶联嘌呤能受体。它在血小板聚集过程中起到重要作用,因此是治疗血栓类疾病的重要靶点。Idorsia公司在两项2期临床试验中检验了selatogrel抑制血小板聚集的能力。
POPular Genetics公布的“A Genotype-Guided Strategy for Oral P2Y12 Inhibitors in Primary PCI”结果为, 在接受直接PCI治疗的STEMI患者中,从12个月净不良复合终点事件(死亡、心肌梗死、卒中、支架内血栓或PLATO大出血标准)的角度看,基因型CYP2C19指导的P2Y12用药12个月预后非劣效于标准治疗(替格瑞洛或普拉格雷), 5.1% vs.5.9,p for noninferiority <0.001。
尽管次要终点分析结果显示,根据PLATO、BARC type 3-5和TIMI大出血标准,基因型指导的P2Y12用药与大出血的改善之间不存在统计学相关性,但根据PLATO标准,基因型指导的P2Y12用药组12个月中大出血或轻微出血的发生率显著低于标准治疗组(9.8% vs. 12.5%, p=0.04)。
相关研究拓展阅读:
2009年PLATO Trail提出替格瑞洛可显著减少急性冠脉综合征(ACS)患者不良心血管事件发生率“Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes”。
2019年6月“Updated Expert Consensus Statement on Platelet Function and Genetic Testing for Guiding P2Y12 Receptor Inhibitor Treatment in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention"
进一步更新了在根据指南推荐实施DAPT治疗外,如何结合临床和手术指征,使用血小板功能检测(platelet function testing ,PFT)和基因检测(genetic testing)指导个体化P2Y12降阶梯/升阶梯治疗的共识方法,指导思路详见下图。
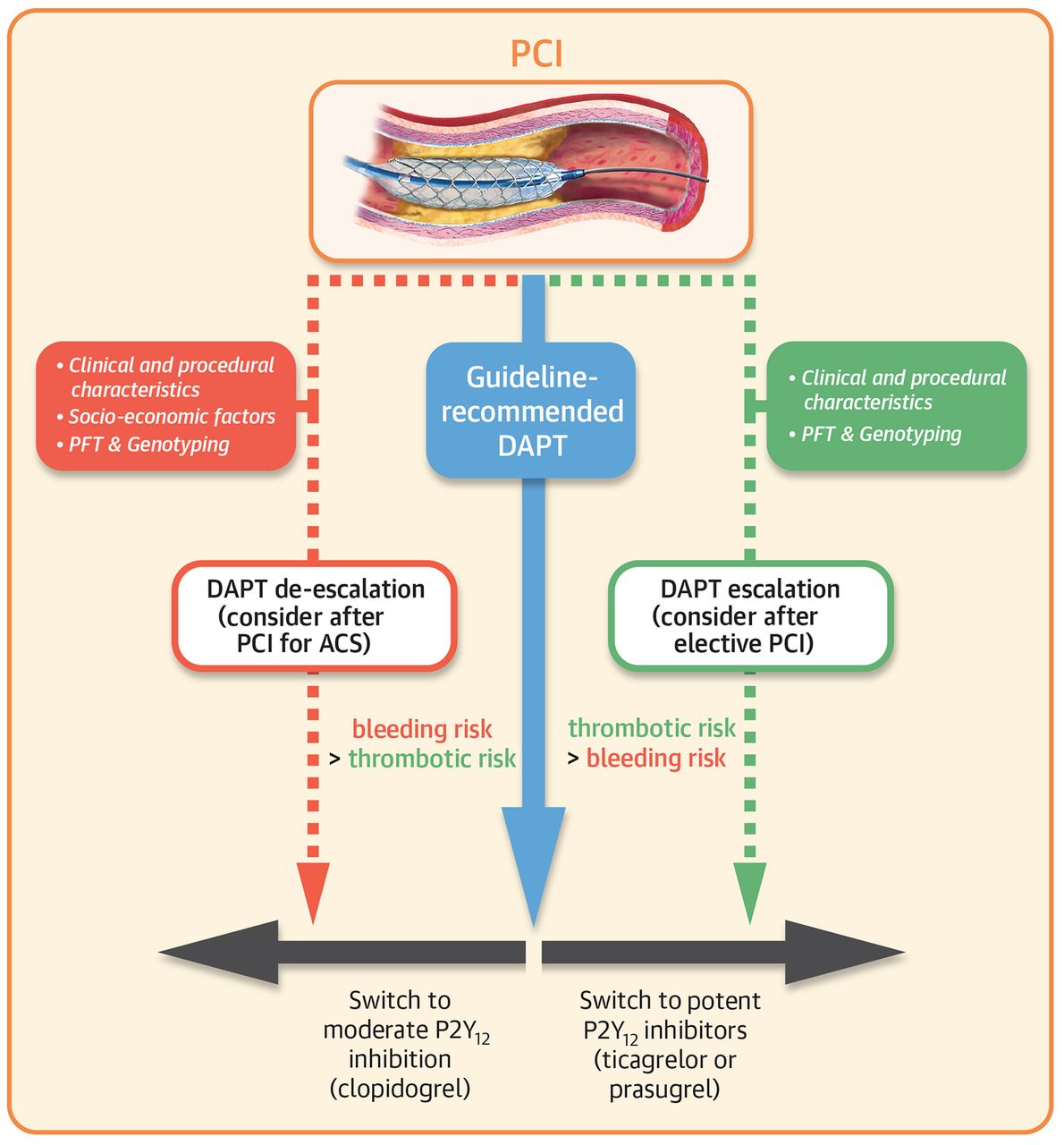
不同基因类型对P2Y12的耐药分析可详见“DAPT, Our Genome and Clopidogrel”。
ESC 2019上发布的最新有关P2Y12的证据已同步到前期导读文章《双抗治疗, 一把锋利的双刃剑 》。
方法