科学研究
Expert Opinion
JOURNAL:ACC Article Link
Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, FACC
The following are key points to remember from this review on anticoagulation in concomitant chronic kidney disease (CKD) and atrial fibrillation (AF):
1. AF and CKD often coexist as they share multiple risk factors, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and coronary artery disease.
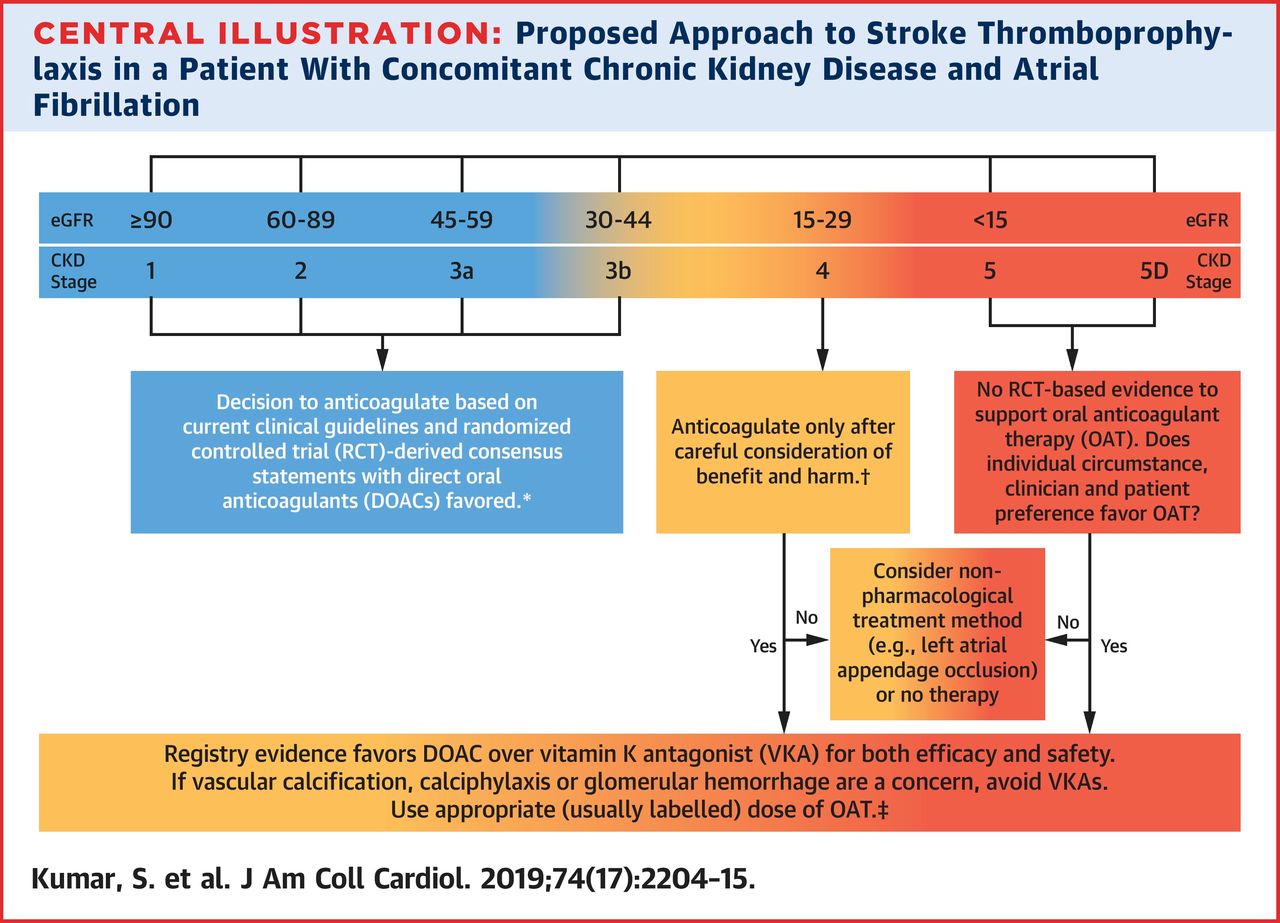
2. Although there is irrefutable evidence supporting anticoagulation in AF in the general population, these data may not necessarily be applicable in the setting of advanced CKD, where the decision to commence anticoagulation poses a conundrum.
3. Among patients with CKD, there is a progressively increased risk of both ischemic stroke and hemorrhage as renal function declines, complicating the decision to initiate anticoagulation.
4. No definitive clinical guidelines derived from randomized controlled trials exist to aid clinical decision making, and the findings from observational studies are conflicting.
5. The limited available data suggest that direct oral anticoagulants should generally be favored over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) in view of their probable increased safety and efficacy in CKD, with a lower risk of vascular calcification and anticoagulant-associated nephropathy.
6. Although there are limited efficacy and safety outcome data, both the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency have approved reduced doses of apixaban, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate 15-30 ml/min; the FDA has also approved the use of a specific low-dose dabigatran (75 mg twice daily), based solely on pharmacokinetic data, for these patients.
7. The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations (2018) concluded that there is insufficient high-quality evidence to recommend VKAs for prevention of stroke in CKD stage 5 patients with AF, especially when balancing the significant risks of bleeding, accelerated vascular calcification, and calcific uremic arteriopathy associated with VKA therapy.
8. More recently, there was an updated 2019 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Rhythm Society focused update guideline for the management of patients with AF; in this report, there was a soft recommendation for using anticoagulation with either warfarin or apixaban with the caveat “but further study is warranted.”
9. Until dedicated randomized clinical trials are completed, to define optimal management, clinical decision making should be informed by the limited data available, which necessitates individualization and physician-patient collaboration and discussion.
10. A rigorous discussion of the risk and benefits of anticoagulation, taking into account patients’ characteristics and preferences, is important to decide on appropriate management. If anticoagulation is not initiated, the viability of a nonpharmacological treatment such as left atrial appendage occlusion may be considered, or whether in fact no therapy is the best choice for that individual patient.