
Pre-reading
影响冠状动脉性心脏病的预后因素
CBSMD
除了不同的干预方式(EXCEL研究 CABG vs.PCI)、介入术式(单支架术vs.双支架术等)和介入器械(裸金属支架 vs.药物洗脱支架)对心血管疾病干预预后存在影响外:
*“Current Interventions for the Left Main Bifurcation”
* 《EXCEL Trail - 左主干血运重建的最新证据》
前期经过多项RCT汇总数据分析及原创研究筛选出的可能对预后产生影响的因素还包括:
采用高敏肌钙蛋白明确两性心梗诊断中的阈值差异
* 扩展阅读《医疗机构及临床医生应如何设置与解读Hs-cTn?》
心血管老化
两性差异
* 前期有研究提示两性的置入支架预后或有不同,女性患者多表现为左主干开口病变,而男性更倾向罹患左主干分叉病变,尽管左主干病变特点呈现两性差异,但中期预后经“Sex differences in left main coronary artery stenting: Different characteristics but similar outcomes for women compared with men”研究证实首要复合终点(全因死亡、MI或卒中)无差异(10.8% vs. 10.8%, respectively, log-rank p=0.587); TLR女性高于男性(8.8% vs. 5.7%, respectively, p<0.05)。
* 2020年4月发表在JACC上的5年研究提示由心源性死亡、缺血驱动靶病变血运重建(ID-TLR)或MI组成的复合终点以及单独的ID-TLR的预后数据存在两性差异"Long-Term Outcomes in Women and Men Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention",数据详见下图
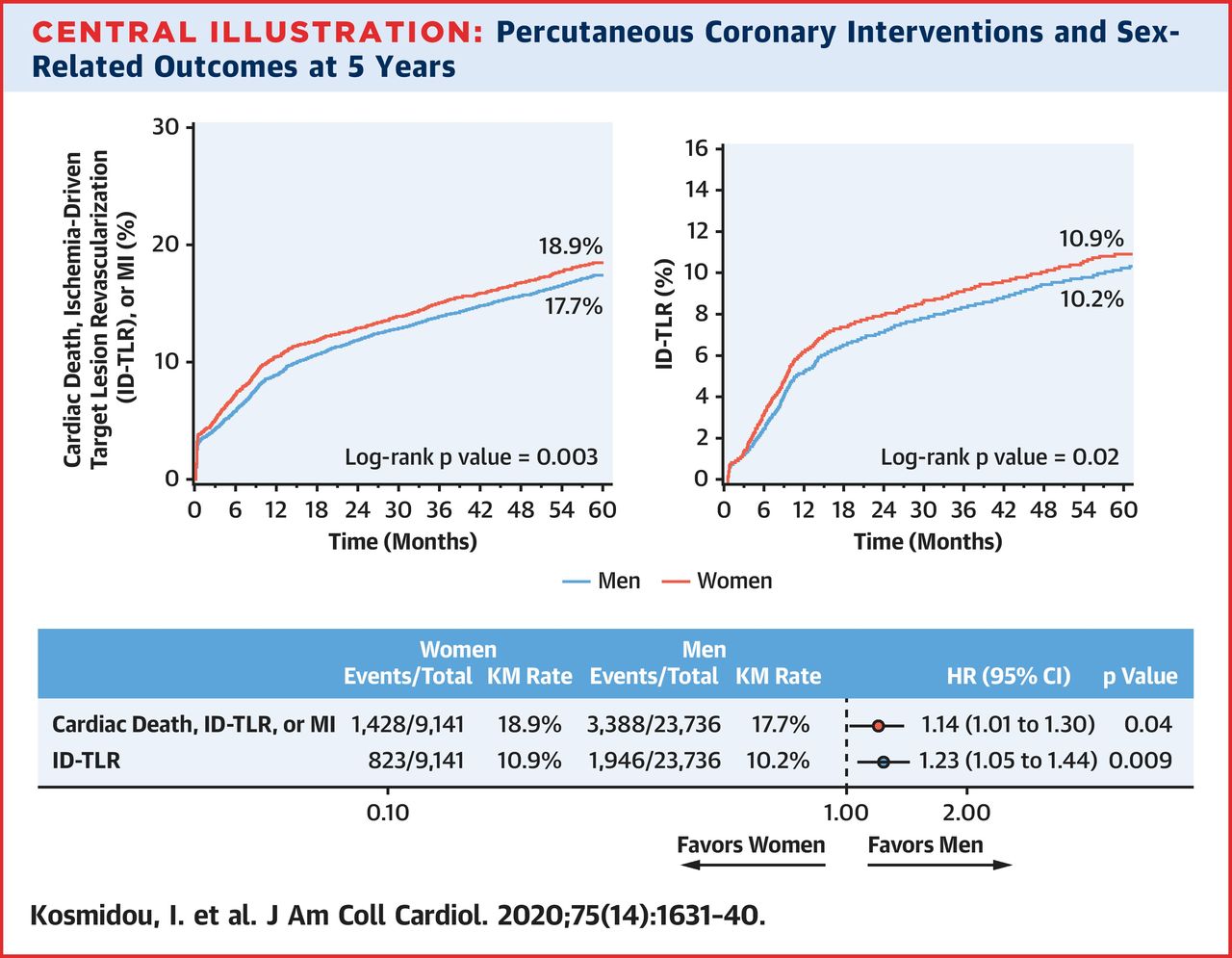
年龄≥65急性STEMI女性患者心梗预后区别于男性和更年轻的女性
- 女性STEMI患者对比男性患者的治疗与护理差异
* “Twenty Year Trends and Sex Differences in Young Adults Hospitalized With Acute Myocardial Infarction”
- 采用性别差异性护理可改善预后“4-Step Protocol for Disparities in STEMI Care and Outcomes”
- 院外护理模式对预后的影响
* “Sex differences in discharge destination following acute myocardial infarction”
Co-morbidity
不管是接受CABG治疗还是PCI,女性患者区别于男性患者的临床差异指向了多种合并症
* 糖尿病直接作用于预后“Obesity, Diabetes, and Acute Coronary Syndrome: Differences Between Asians and Whites”
* 心肌梗死合并心源性休克可参阅《急性心肌梗死合并心源性休克,临床上的一块烫手山芋》
心肌梗死面积
血管阻塞程度对ST段抬高ACS患者预后的影响
*“Long-term survival and causes of death in patients with ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome without obstructive coronary artery disease”
* 扩展阅读《AHA 2019 MINOCA科学声明及摘要》
血流储备分数
* 可参阅《冠状动脉CT血管成像的血流储备分数》
CTO
成功的CTO可改善预后,左心室收缩功能障碍(LV EF ≤ 40%)患者的预后差于左心室收缩功能正常的患者
* 扩展阅读《冠状动脉慢性完全性闭塞病变PCI & 冠脉穿孔》
* 扩展阅读《慢性闭塞病变之CTO PCI与OMT之间的抉择》
* 扩展阅读影响CTO成功率的《心肌桥》
穿孔
穿孔发生率虽低,且与患者基线相关,但确会影响冠脉干预预后:
心绞痛症状和心肌缺血对的SCAD的预后影响
心梗后Galectin-3水平对预后的影响
*“Galectin-3 Levels and Outcomes After Myocardial Infarction: A Population-Based Study”
* 扩展阅读《Galectin-3对心肌梗死后死亡与心衰的预测价值》
PCI过程中影像学指导完善手术结果对预后的改善性作用:
* 是否采用影像学指导
* 最小管腔面积 “Prognostic Value of Intravascular Ultrasound in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease”
穿刺部位
无保护左主干介入的穿刺部位
介入术后的抗凝、抗血小板策略
- 可参阅《双抗治疗, 一把锋利的双刃剑》和《基因型指导口服P2Y12抑制剂策略》
呼吸道疾病对心血管预后的影响
- “Association of Cardiovascular Disease With Respiratory Disease”
心源性猝死可参阅《可穿戴复律除颤仪 & 心源性猝死》
不明原因死亡可参阅《心脏代谢临床试验中的黑洞 —— 不明原因死亡》
以上文献不能完全囊括所有相关文献(不含阴性结果),仅从各研究方向入手,后续将陆续更新,欢迎点击每篇文献的标题在CBSMD科学图书馆内拓展阅读。
Long-Term Outcomes in Women and Men Following Percutaneous Coronary ...
JACC | Apr 09,2020
Sex-Specific Thresholds of High-Sensitivity Troponin in Patients With S...
J Am Coll Cardiol. | Oct 17,2019
Association of Cardiovascular Disease With Respiratory Disease
J Am Coll Cardiol. | Mar 05,2019
Access Site and Outcomes for Unprotected Left Main Stem Percutaneous C...
JACC Cardiovasc Interv. | Jan 16,2019
Prognostic Value of Intravascular Ultrasound in Patients With Coronary Ar...
JACC | Oct 19,2018
Sex differences in discharge destination following acute myocardial infarctio...
Coron Artery Dis. | Sep 07,2018
Outcomes After Coronary Stenting or Bypass Surgery for Men and Women W...
JACC Cardiovasc Interv. | Jul 06,2018
4-Step Protocol for Disparities in STEMI Care and Outcomes in Women
J Am Coll Cardiol. | May 11,2018
Impact of the US Food and Drug Administration–Approved Sex-Specific C...
Circulation. | Apr 24,2018
Sex differences in left main coronary artery stenting: Different characterist...
Int J Cardiol. | Jan 10,2018
Long-term survival and causes of death in patients with ST-elevation acute ...
Eur Heart J. | Aug 27,2018
Comparison of Delay Times Between Symptom Onset of an Acute ST-ele...
Am J Cardiol. | Feb 11,2018
IVUS Guidance Is Associated With Better Outcome in Patients Undergoin...
Circ Cardiovasc Interv. | Aug 16,2017
Current Interventions for the Left Main Bifurcation
JACC Cardiovasc Interv. | Aug 21,2017
Mortality Following Cardiovascular and Bleeding Events Occurring Beyond ...
JAMA Cardiol. | Aug 22,2017
Benefit of switching dual antiplatelet therapy after acute coronary syndrome:...
Eur Heart J. | Sep 12,2017
Relationship Between Infarct Size and Outcomes Following Primary PCI...
J Am Coll Cardiol. | Nov 23,2017
Sex Differences in Clinical Profiles and Quality of Care Among Patients...
J Am Heart Assoc. | Feb 12,2018
Prevalence of anginal symptoms and myocardial ischemia and their effect on ...
JAMA Intern Med. | Jul 31,2019