推荐文献
Review Article2017 Aug 1;70(5):590-606.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
van der Harst P, de Windt LJ, Chambers JC Keywords: EWAS; HAT; HDAC; RNA; histones; methylation
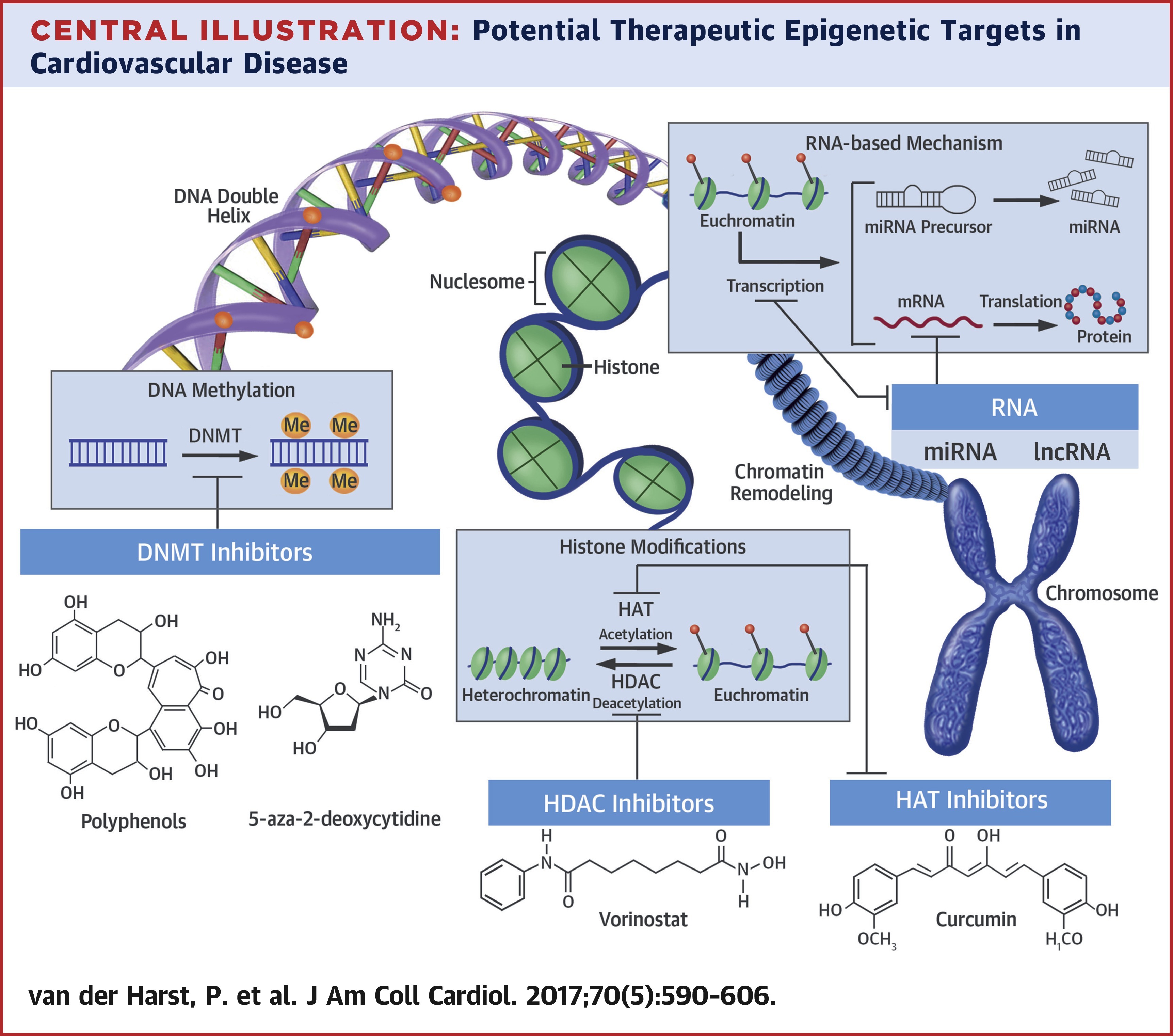
A plethora of environmental and behavioral factors interact, resulting in changes in gene expression and providing a basis for the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Heterogeneity in gene expression responses among cells and individuals involves epigenetic mechanisms. Advancing technology allowing genome-scale interrogation of epigenetic marks provides a rapidly expanding view of the complexity and diversity of the epigenome. In this review, the authors discuss the expanding landscape of epigenetic modifications and highlight their importance for future understanding of disease. The epigenome provides a mechanistic link between environmental exposures and gene expression profiles ultimately leading to disease. The authors discuss the current evidence for transgenerational epigenetic inheritance and summarize the data linking epigenetics to cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, the potential targets provided by the epigenome for the development of future diagnostics, preventive strategies, and therapy for cardiovascular disease are reviewed. Finally, the authors provide some suggestions for future directions.