Pre-reading
The following are key points to remember from this state-of-the-art
review on transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and the role of
multimodality imaging in common and complex clinical scenarios:
-
1. TAVR has rapidly become an established therapy for patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis (AS).
-
2. Technological advances and the
learning curve have resulted in better procedural results in terms of
hemodynamic valve performance and intermediate-term clinical outcomes.
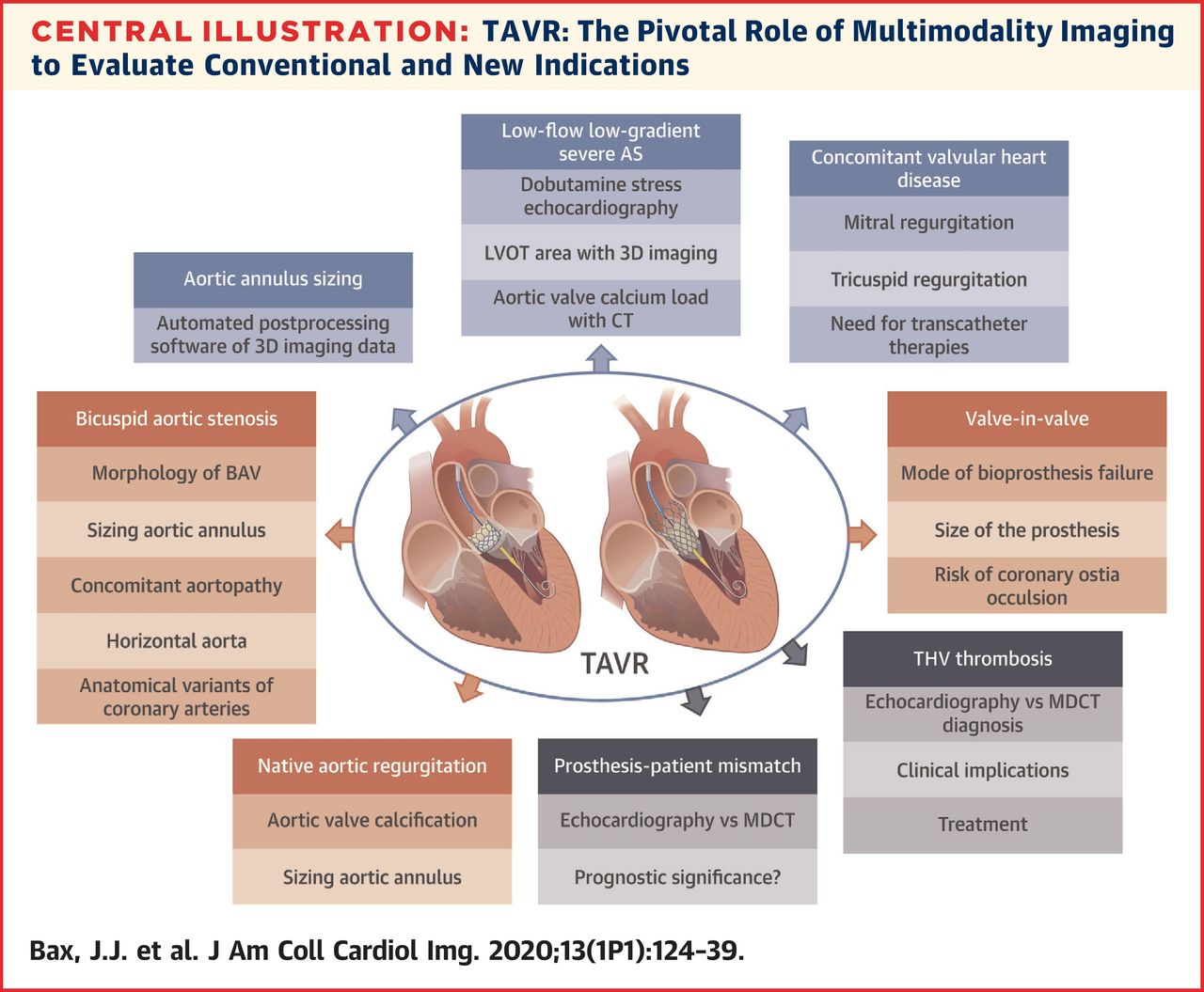
-
3. The integration of anatomical and
functional information provided by multimodality imaging has improved
size selection of TAVR prostheses, permitted better patient selection,
and provided new insights in the performance of the TAVR prostheses at
follow-up.
-
4. The use of 3D imaging techniques
(multi-detector row computed tomography [MDCT], cardiac magnetic
resonance [CMR], and 3D echocardiography) that permit accurate
measurement of the left ventricular outflow tract area by direct
planimetry has demonstrated the ability to reclassify severe AS patients
into moderate AS by 12% in patients with low-flow, low-gradient severe
AS.
-
5. Furthermore, the field of TAVR
continues to develop and expand the technique to younger patients with
lower risk on the one hand, and more complex clinical scenarios, on the
other hand, such as degenerated aortic bioprostheses, bicuspid aortic
valves, or pure native aortic regurgitation.
-
6. The use of both echocardiography
and MDCT is key in the diagnosis of patients with severe AS who may
benefit from TAVR as well as in the procedural planning and evaluation
of the results at follow-up.
-
7. The number of patients with
bicuspid AS treated with TAVR is increasing and the TAVR results with
the use of new generation prostheses are promising.
-
8. TAVR in degenerated bioprosthesis
has been an important recent breakthrough because re-operation in these
individuals is associated with very high mortality.
-
9. Patients with native aortic regurgitation are also now being treated with TAVR.
-
10. These newer indications for TAVR
need careful imaging evaluation of the anatomy of the landing zone to
ensure successful anchoring of the TAVR prosthesis and to minimize
complications. These new horizons for TAVR are making multimodality
imaging critically important for this evolving therapy.